Page 16
Notes:
Journal of Biomedical Research | ISSN: 0976-1683 | Volume 30
allied
academies
March 14-15, 2019 | London, UK
T issue Engineer ing, Stem Cel ls and Regenerat ive Medicine
Cel l and Gene Therapy
World Congress on
International Conference on
&
Joint Event
K
3intaro Flexy program is a combination of 3 treatment
and rehabilitation methods: The injection of Kintaro Cells
(allogenic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells), taping and
therapeutic gymnastics according to themethods and protocols
of Kintaro Cells Power Japan. Orthopedic diseases take the first
place in theWorld: Osteochondritis – chronic diseases or pain in
the spineor joints, trauma, curvatureof the spine in childrenand
adults, flat-footedness etc. We propose a new non-surgical way
to restore the functionality of the motor segments of a person
with the help of stem cells. The creation of the Kintaro Flexy
program is a result of combined 50-year experience in stem
cell research in Japan and Russia, 20-year practical experience
in sports rehabilitation and 8-year experience in elastic taping.
We have created a program for treatment and rehabilitation.
Kintaro Flexy is easy to use and effective (total efficiency – 98%
(95 treatments in 2017)). Today this program is used not only by
orthopedists but also by many cosmetic clinics.
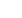
Speaker Biography
Aleksandr Proshkin took a Doctor of Medicine degree at the age of 23 at the Ural state
medical academy in Russia. He is currently the medical director of Kintaro Cells Power
Japan. He has 20 years of practical experience in sports medicine and orthopedics. He
is a winner of Russian Federation’s state award. He has published 18 articles, conducted
morethan50workshops,developed5 intelligentprogramsamongwhich isKintaroFlexy.
e:
doctoraleksandr@cellspower.comAleksandr Proshkin
Kintaro Cells Power, Japan
Kintaro Flexy – spine-joints recovery program
Aleksandr Proshkin
, Biomed Res, Volume 30
DOI: 10.4066/biomedicalresearch-C1-024