Page 26
Notes:
allied
academies
Nov 12-13, 2018 | Paris, France
Joint Event
Nutraceuticals and Food Sciences
International Conference on
27
th
International Conference on
Nursing and Healthcare
&
Journal of Food science and Nutrition | Volume 1
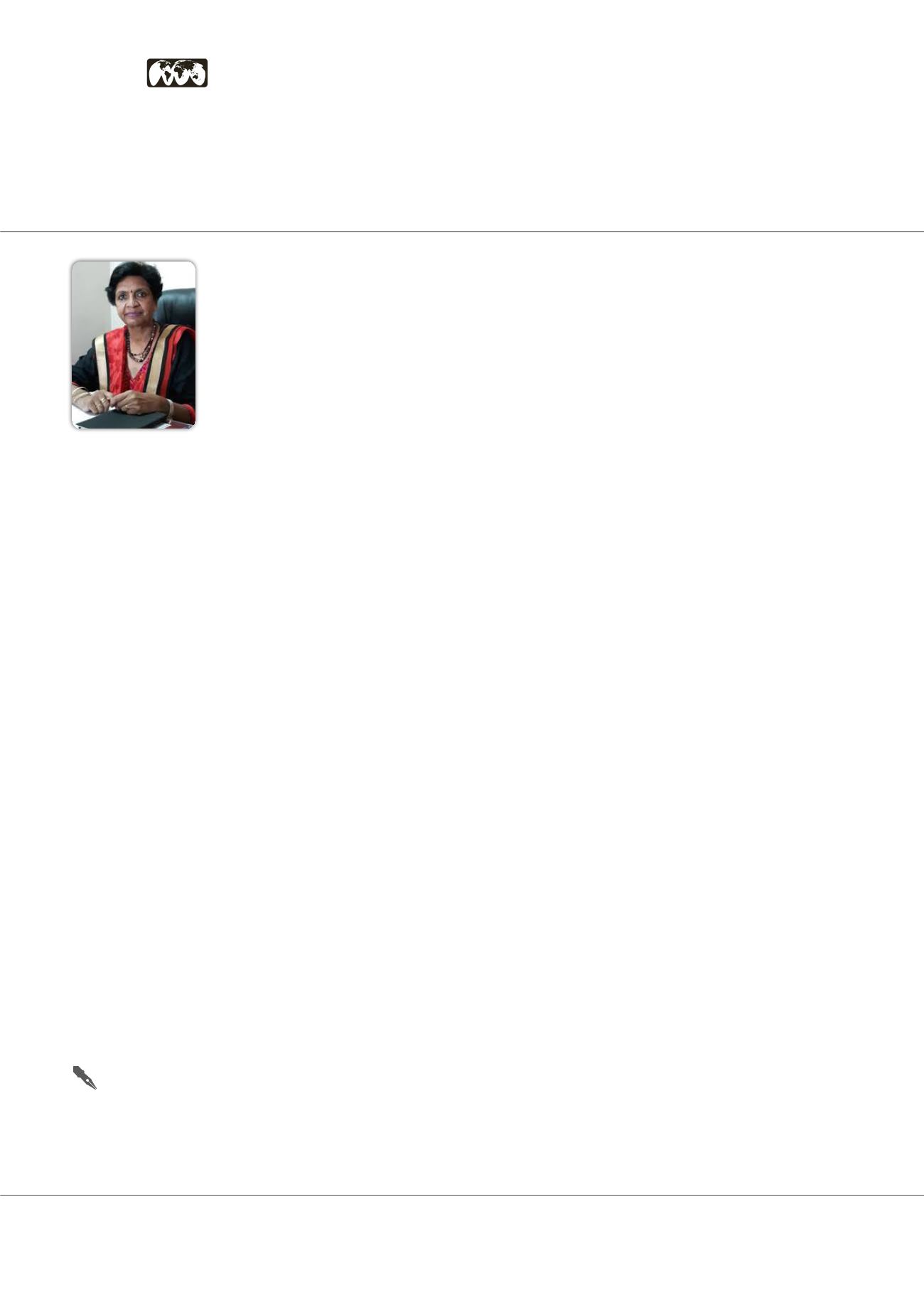
Jyoti D Vora
Ramnarain Ruia College, India
Waste utilization by Biotransformation of carica papaya linn peels and development of
a value-added product from obtained by-products: An organoleptic and biochemical
approach
T
he diverse agro-climatic zones make India as the second
largest producer of fresh fruits and vegetables granting
processed fruit and vegetable products such as juices,
preserves etc. to number along that leads to the generation
of large amounts of wastes, both solid and liquid. This
waste is incautiously being thrown without any treatment
promoting environmental deterioration. However, these
wastes hold immense potential nutritionally; functionally as
well as physicochemical which can be utilized for producing
cheaper value-added ingredients that bear economic
benefits. Carica papaya Linn is a wholesome fruit, widely
known as “the Fruit of Angels”, serves as an ideal, low cost
food. It ranks second as a source of beta-carotene and is an
excellent source of natural sugars, vitamin C, and potassium,
with fair amounts of calcium and phosphorus. Low in
calories, this exotic fruit holds immense medicinal value
since ancient times for treating innumerable disorders and
conditions like toothache up to the prevention of cancer.
To substantiate the potential of fruit wastes, proximate
profiles of papaya peel were analysed using bench science
experiments. Following analysis, the peels were then bio
valorised to procure commercially important acetic acid
which in its own holds several health benefiting attributes.
Further in order to project the organoleptic appeal of the
fruit vinegar under study, invasive and non-invasive sensory
evaluation was carried out by a semi-trained panellist. This
was executed with a recipe. The data was subjected to
biostatistical analysis which proved that the novel recipe was
highly appreciated. Critical control points were established
during the process of novel product development and
hazard analysis at critical control points was carried out. The
commercial appeal of the recipe was also speculated using
value for money (VFM) studies. Future prospects include
determination of anti-nutrients and anti-microbial activity
of vinegar. The use of this waste utilized novel product as a
functional food and development of novel products keeping
in mind the nutritional profile and organoleptic acceptance
needs to be explored.
Speaker Biography
Jyoti D Vora is an Academician, Head of The Department, Consultant, Trainer, Research
Guide And Researcher in Biochemistry And Food Science And Quality Control and her
qualifications are
M.Sc., PhD,
F.S.Sc., MASFFBC, CME (USA), NET Cleared, Nutritional
consultant at Raleigh Medical Centre, North Carolina, Certified Functional Foods
Scientist (FFC,USA).
e:
drjyotidvora@gmail.com