allied
academies
Materials-Metals 2017
Page 40
November 16-17, 2017 Paris, France
13
th
Annual Conference on
Materials Science, Metal and Manufacturing
Journal of Materials Science and Nanotechnology
Volume 1 Issue 2
Electrochemical fabrication of V-4Cr-4Ti alloys
from the mixed oxides in a eutectic CaCl
2
-NaCl
melt
Xiaozhou Cao
1,2
, Qiuyue Li
1,2
, Yuanyuan Shi
3
, He Yang
1,2
, Tao Jiang
1,2
and
Xiangxin Xue
1,2
1
Northeastern University, China
2
Key Laboratory of Recycling Science for Metallurgical Resource, China
3
Chinalco Shenyang Non-ferrous Metal Processing Co., Ltd, China
V
-4Cr-4Ti alloys exhibit important advantages as a
candidate structural material for fusion reactor first-wall
and blanket applications. V-4Cr-4Ti alloys were prepared
by direct electrochemical reduction of the solid mixture
of V
2
O
3
, Cr
2
O
3
and TiO
2
in molten CaCl
2
-NaCl melt at
1073K. The influence of cell voltage and electrolysis time on
the electrolysis process was reported. The microstructure
and phase compositions of the products were analyzed by
scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction
(XRD) during the electrolysis process. The results showed
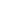
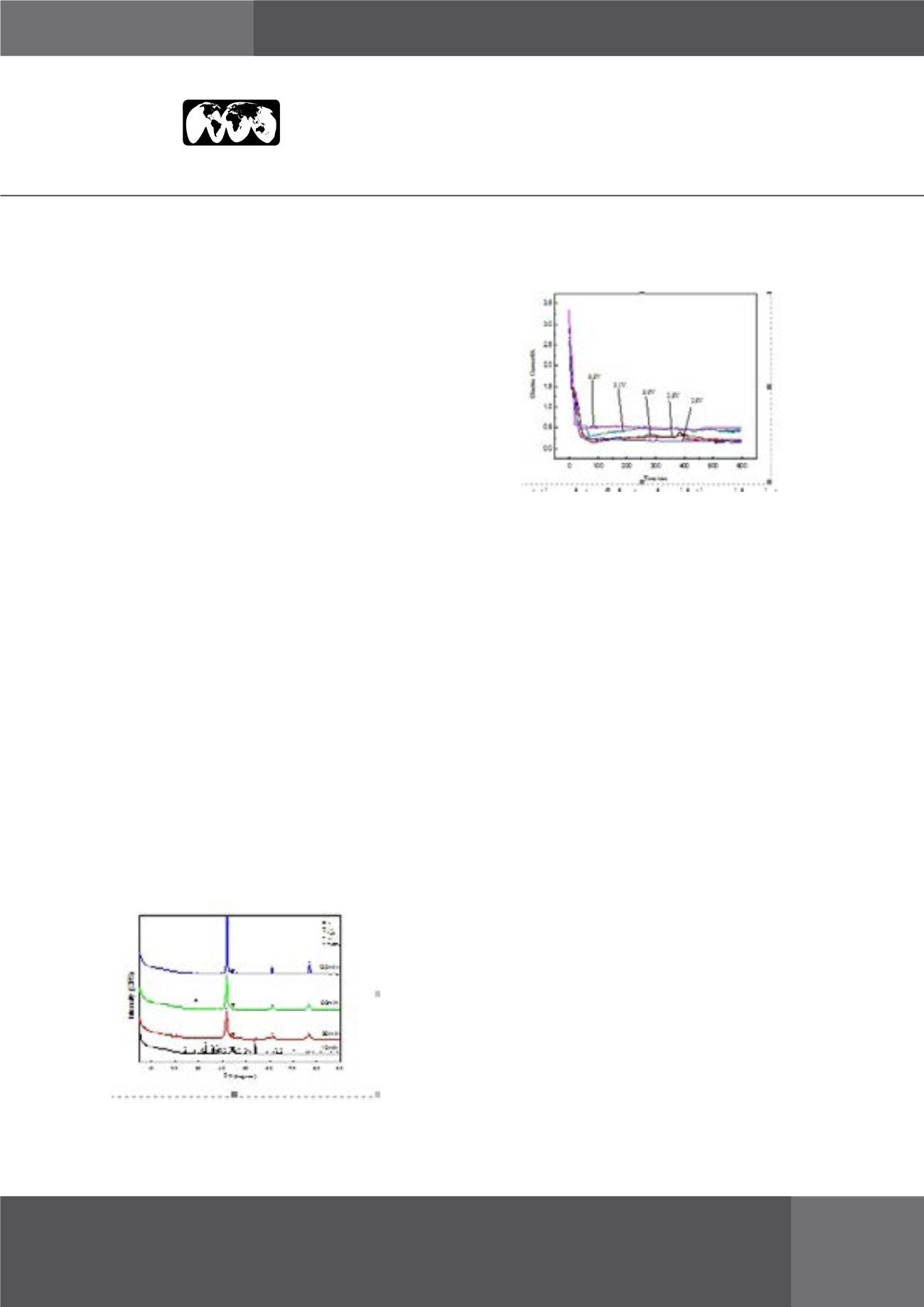
that V-4Cr-4Ti alloys can be obtained at the voltage of 3.1V
and the time of 0.5h. The reduction process involved Cr
2
O
3
was reduced to Cr metal firstly, thereafter V
2
O
3
and TiO
2
was
reduced to low-valence oxide of vanadium and titanium.
The reduction rate increases with increasing cell voltage, lots
of perovskite oxide formed during the electrolysis process.
With the increase of the voltage, electrochemical reduction
rate increased on the surface of electrode, the current rapidly
decreased, and finally reached a stable value at a short time,
which is beneficial to accelerate the transferring of oxygen
ions. With the increase of time, the particles size of new
generated product is less than1μm after 120min of electrolysis
it becomes smaller and uniform.
Figure 1:
XRD patterns of the products at different electrolysis
time.
Figure 2:
Current-time plots of electro-deoxidation oxide
mixture at different electrolytic voltage.
Recent Publications
• Barabash V, Federici G, Linke J, Wu C H (2003) Material/
plasma surface interaction issues following neutron
damage. Journal of Nuclear Materials. 313-316:42-51.
• Xiao W, Wang D H (2014) The electrochemical reduction
processes of solid compounds in high temperaturemolten
salts. Chemical Social Reviews. 43(10):3215-3228.
• Kar P, Evans J W (2008) A model for the electrochemical
reduction of metal oxides in molten salt electrolyte.
Electrochimica Acta 54:835-843.
• Juzeliunas E, Cox A, Fray D J (2012) Electro-deoxidation
of thin silica layer in molten salt-Globular structures
with effective light absorbance. Electrochimica Acta
68:123-127.
• Alexander D T L, Schwandt C, Fray D J (2011) The
electro-deoxidation of dense titanium dioxide precursors
in molten calcium chloride giving a new reaction
pathway. Electrochimica Acta.56:3286-3295.
Biography
Xiaozhou Cao received his BS in 2003, MS and PhD degrees in 2008 with
Professor Zhuxian Qiu from Institute of Nonferrous Metallurgy at Northeastern
University. He joined the Institute of Metallurgical Resources and Environmental
Engineering at Northeastern University since 2008. His current research
focuses on molten salt and ionic liquid electrochemistry to seek a simple and
environmentally friendly way to produce the corresponding parent metals and
alloys.
caoxz@smm.neu.edu.cnXiaozhou Cao et al., Mater Sci Nanotechnol 2017, 1:2