allied
academies
GREEN CHEMISTRY &
TECHNOLOGY
7
th
International Conference on
J u n e 1 8 - 2 0 , 2 0 1 8 | D u b l i n , I r e l a n d
Journal of Industrial and Environmental Chemistry
|
Volume 2
Page 23
Note:
cellulose hydrolysis at 140, 150, 160 and 170°C respectively. This paper will present the development of BAIL based
artificial cellulase type catalysts, QSAR studies, catalyst immobilizations, applications on lignocellulosic biomass
materials (corn stover, switchgrass, poplar) and recycling studies.
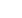
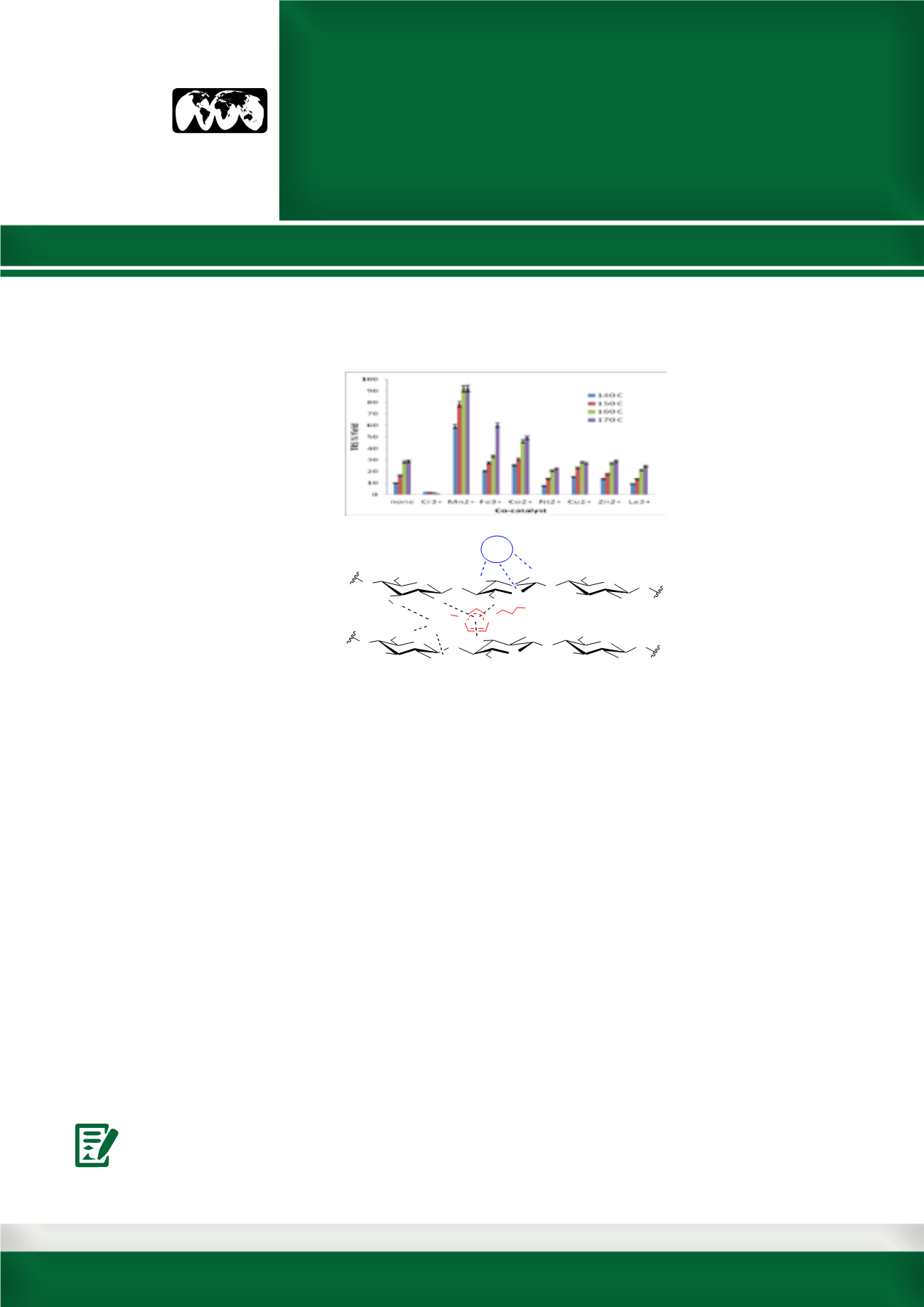
Figure 1: The total reducing sugar (TRS)% yields produced during the hydrolysis of cellulose (DP~450) in aq.
1-(1-propylsulfonic)-3-methylimidazolium chloride (0.0321 mol H+/L), at 140-170°C, 3h, using metal chlorides
([Mn+]=20 mol% of glucose eqv.) as co-catalysts and possible interactions of catalysts with cellulose.
N N
H
3
C
SO
3
O
O
O
O
O
OH
O
HO
OH
O
O
O HO
OH
O
OH
Cl
O
O
HO
OH
O
OH
O
O
OH
OH
O
O HO
OH
O
OH
H
H
H
H
H
_
+
_
+
M
n+