Page 8
Notes:
allied
academies
Nov 22-23, 2018 | Paris, France
Joint Event
Nutrition and Health
16
th
International Conference on
26
th
International Conference on
Diabetes and Endocrinology
&
Journal of Insights in Nutrition and Metabolism | Volume 2
C
hronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of obesity,
which is associated with metabolic dysfunction and insulin
resistance.Guthormoneghrelinpromotes food intake, adiposity
and insulin resistance; and ghrelin is functions through ghrelin
receptor, Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor (GHS-R).
To determine the direct effect of GHS-R in macrophages, we
generated myeloid-specific GHS-R knockout mice and studied
them under chronic and acute inflammatory conditions of diet-
induced obesity (DIO) and endotoxin lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
treatment. Suppression of GHS-R in myeloid cells attenuated
DIO-associated obesity, DIO-induced insulin resistance, and LPS-
induced inflammation. The myeloid-specific GHS-R knockout
mice showed significant reductions of pro-inflammatory
cytokines in the circulation, and pro-inflammatory gene
expression in liver, fat and skeletal muscle. To investigate the
underpinning mechanism, we isolated bone-marrow-derived-
macrophages (BMDM). GHS-R deficient BMDM showed a
polarization profile toward anti-inflammatory M2. These
data suggest that GHS-R deficiency promotes macrophage
anti-inflammatory shift by modulating insulin signaling and
mitochondrial energetics. Collectively, our findings indicate
that suppression of GHS-R in myeloid-cells promotes anti-
inflammatory polarization, decreases inflammatory responses
of both diet-induced chronic inflammation and LPS-induced
acute inflammation, prompting a healthier lean and insulin
sensitive state. Thus, macrophage GHS-R has profound effects
on lipid metabolism and inflammation, is a critical molecular
link that mediates the cross-talks between immunity, lipid
metabolism, inflammation and insulin sensitivity.
Speaker Biography
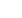
Yuxiang Sun is an associate professor at Nutrition and Food Science at Texas A&M
University, USA. She obtained her PhD from University of Manitoba, Canada. She is
a leader in ghrelin research; ghrelin is an important nutrient sensor and metabolic
regulator. She has over 65 peer-reviewed publications, many of which are in premier
journals such as Cell Metabolism, PNAS, JCI, Diabetes and Aging Cell. Her publications
have been cited over 4413 times, and her publication H-index is 29. She is serving as an
editorial board member of a number of nutrition and metabolic journals.
e:
Yuxiang.Sun@tamu.eduYuxiang Sun
Texas A&M University, USA
Macrophage ghrelin receptor - A novel regulator for lipid metabolism and
inflammation