Page 32
Notes:
Mater Sci Nanotechnol 2017 | Volume 1 Issue 2
allied
academies
Nanomaterials and Nanochemistry
November 29-30, 2017 | Atlanta, USA
International Conference on
E
psilon iron oxide (ε-Fe
2
O
3
) is one of polymorphs of Fe
2
O
3
,
which generates as a stable phase in nanometer size region.
Our research group has reported the first synthesis of pure
ε-Fe
2
O
3
by using a chemical nanoparticle synthesis method.
ε-Fe
2
O
3
has a strong magnetic anisotropy, and thus exhibits a
large magnetic coercive field of 25 kOe at room temperature,
which is the largest value among magnetic metal oxides. In this
presentation, we report the synthesis of metal subsutituted
ε-Fe
2
O
3
(ε-M
x
Fe
2
−xO
3
), crystallographic orientation of
ε-M
x
Fe
2
−xO
3
nanoparticles, and metal substitution effect on
the magnetic properties. Especially, rhodium subsutitution
enlarges the magnetic coercive field up to 35 kOe. Due to the
large magnetic anisotropy, ε-Fe
2
O
3
and ε-M
x
Fe
2
−xO
3
show the
electromagnetic wave absorption in a millimeter wave region
of 35–222 GHz, which is the highest frequency electromagnetic
wave absorption caused by the zero-field ferromagnetic
resonance (natural resonance). The present materials are to be
useful for recently developed millimeter wave technology such
as car radar and high-speed wireless communication.
Speaker Biography
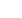
Asuka Namai is currently an Assistant Professor of Department of Chemistry, School of
Science at The University of Tokyo. She received her Ph.D in Science at the University
of Tokyo, Japan, in 2013. Her research focuses on the development and physical and
chemical characterization of functionalized nanomaterials, with particular interest in
iron oxide-based nanomagnets and magnetism.
e:
asuka@chem.s.u-tokyo.ac.jpAsuka Namai
The University of Tokyo, Japan
Large coercive field and high-frequency millimeter wave absorption in metal-
substituted ε-iron oxide nanomagnet