Page 18
Notes:
allied
academies
February 25-26, 2019 | Paris, France
Materials Science and Engineering
2
nd
International Conference on
Journal of Materials Science and Nanotechnology | Volume 3
W
e aim at encapsulating fragrances made of a variety
of lipophilic species to slow down their diffusion. Our
strategy is to develop capsules by polymerizing the water
intermediate phase of an oil-in-water-in-oil double emulsion.
In other terms, our system consists in a direct emulsion of
fragrance (O1) in a water phase (W) containing monomer,
initiator and crosslinker. To obtain the double emulsion, this
direct emulsion, stabilized by a hydrophilic surfactant, is itself
dispersed in an external lipophilic solvent used in perfumery
(O2) and stabilized by a lipophilic surfactant. Polymerization of
the intermediate water phase aim at obtaining a 3D network.
This strategy exhibits the following advantages over other
nowadays proposed capsules: polymerization only takes place
in the water phase owing to the solubility of the monomer
and the obtained 3D network is supposed to play the role of
an effective barrier limiting the diffusion of the inner lipophilic
species towards either the external solvent or air.
Such a strategy implies combining formulation for the
elaboration of the double emulsion using two antagonistic
surfactants,ahydrophilicandalipophilicone andpolymerization
of the intermediate phase. Insertion of the polymerizable
species in the double emulsion shall not destabilize it. Some
monomers exhibiting interfacial affinity and interfering with
the formulation of the double emulsion have to be avoided. By
varying the nature of the monomers, the initiator to monomer
ratio and the crossliknker to monomer ratio, capsules with
high encapsulation efficiencies and with various mechanical
properties have been obtained.
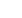
Speaker Biography
Schmitt V is a senior researcher. After a Ph-D in Strasbourg, she moved to Lund in
Sweden for a post-doctoral position before getting hired at CNRS in Nancy with a
permanent position. Since 1998, she is working at Centre de Recherche Paul Pascal
in Bordeaux, France. Her research focuses on the elaboration and characterization of
dispersed model systems like suspensions, emulsions and foams in view of addressing
the link between structure and properties. She has a special interest on emulsions
and foams stabilized by particles and on double emulsions. This presentation is
part of a collaboration she continues with Héroguez V, a CNRS senior researcher
too, specialized in the synthesis of nanoparticles (NPs) by Radical and Metathesis
Polymerizations in dispersed media (suspension, dispersion, mini- microemulsions).
She has high level expertise in Macromolecular Engineering. She has developed
specific methods for producing polymeric NPs exhibiting controlled architecture,
shape, and chemical composition. In particular, pH and thermosensitive NPs have been
designed in order to allow release of active molecules with spatiotemporal control.
e:
schmitt@crpp-bordeaux.cnrs.frSchmitt V
Stasse M and Héroguez V
CNRS University of Bordeaux, France
Elaboration of double emulsion based polymeric capsules for fragrance