allied
academies
Mater Sci Nanotechnol 2017
Volume 1 Issue 3
Magnetic Materials 2017
Notes:
Page 75
October 09-10, 2017 London, UK
International Conference on
Synthesis, structural and electrical characterization
of soft Ni-Cr nanoferrites
Asghari Maqsood
Air University, Pakistan
F
errites which are ferrimagnetic ceramic materials have
different metal oxides converged with iron (Fe
3+
) to form
their core segment. Ferrites are of two kinds, soft and hard.
Soft materials are used for electromagnets because they are
simply magnetized and demagnetized. On the other hand, hard
materials are hard to magnetize and demagnetize, so they are
used for permanent magnets. The core properties of ferrites
depend on composition, synthesis techniques, temperature,
cation distribution and the particle size. Although iron and
metallic alloys are scientifically useful as magnetic materials,
these materials are impractical because of low resistivity at high
frequency. Because of high electrical resistivity of these ferrites,
these are superior at high frequencies. In this talk, the fabrication
of Cr doped Ni
0.5
-Zn
0.5
Cr
x
Fe
2-x
O
4
(0.1≤x≤0.4) is reported. The
material was characterized by x-ray diffraction technique to get
the information related to structure, average crystallite size, x-ray
density, porosity, the specific surface area and surface to volume
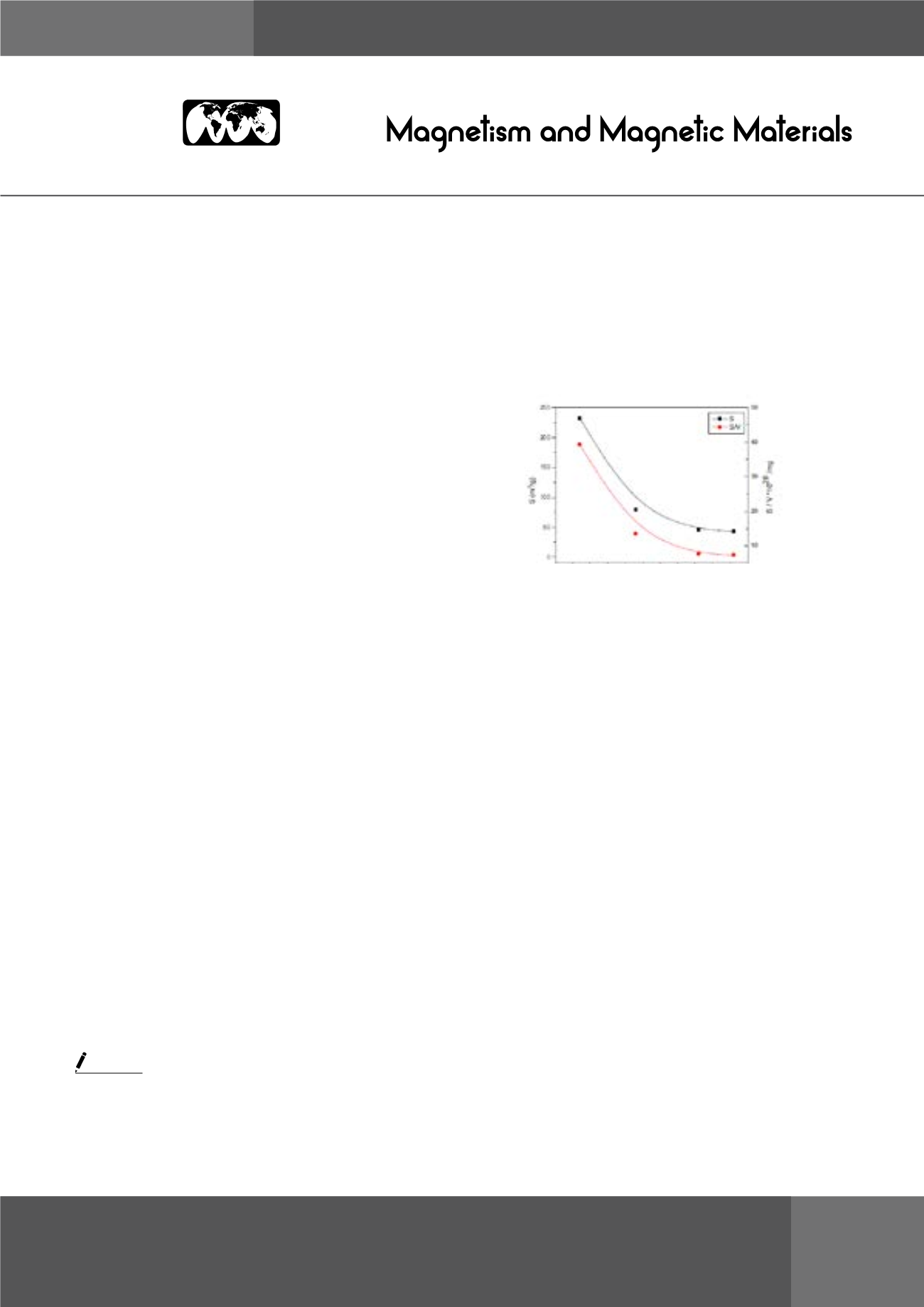
ratio as shown in the Fig. The variation of electrical parameters
like DC electrical resistivity and mobility as a function of
temperature was investigated in the range of 435 to 770 K. The
activation energies of all the samples were calculated from the
DC electrical resistivity data. The dielectric parameters such as
dielectric constant (
ε
), dielectric loss (tanα) and AC conductivity
(α
ac
) are measured in the temperature range of 300 to 770 K. It
was observed that the dielectric constant was found to increase
with the Cr
3+
concentration, while tanα and αac decreased. The
results are explained on the basis of increase in interfacial and
dipolar polarization in the samples. Transition temperatures
obtained from dielectric constant are in agreement with Curie
temperatures, obtained from resistivity plots.
Figure 1:
Variation of the specific surface area to volume ratio
of Ni-Cr nanoferrites
Biography
Asghari Maqsood has her expertise in the fabrication and characterization of
new materials. She prepared single crystals of rare-earth disilicates with the
formula R
2
Si
2
O
7
(R=Tm, Er, Ho, Dy). These materials were characterized
through X-diffraction, magnetic, electrical and dielectric measurements. The
results appeared in the ISI indexed journals, indicating the structural and
importance of these materials from the application and academic interest. She
also has the experience of dealing with high-temperature superconductors,
thin-films of groups II-VI semiconductors and their application in solar cell
technology. She developed a research laboratory namely Thermal Physics at
Quaid-i-Azam University for post graduates, leading to MPhil and PhD degrees.
The research group got involved in the synthesis of nanoferrites and their
characterization almost a decade ago. The researchers have completed their
research projects related to soft and hard nanoferrites for their PhD’s under
her supervision. The materials showed their applications in electronics, utility at
high frequency, mechanical stiffness, etc. The systems CoFe
2
O
4
, Cu/Cd doped
Mg-Zn; Cd doped Ni- ferrites are studied at length and the results are reported
in publications.
tpl.qau@usa.netAsghari Maqsood, Materials Science and Nanotechnology