allied
academies
Page 28
Journal of Materials Science and Nanotechnology
Volume 1 Issue 2
Materials-Metals 2017
November 16-17, 2017 Paris, France
13
th
Annual Conference on
Materials Science, Metal and Manufacturing
Xavier Obradors, Mater Sci Nanotechnol 2017, 1:2
Xavier Obradors
ICMAB-CSIC, Spain
Nanostructured high critical current
superconducting wire research and
development
T
here is a worldwide huge effort in the R&D of high
current superconducting wires for large scale power
applications and magnets which encompasses many
materials science and engineering challenges. Coated
conductors based on epitaxial YBa
2
Cu
3
O
7
(YBCO) films
are one of the most promising alternatives to reach
the required performance goals, as well as to reduce
the cost down to the levels required to make a reality
these technological expectances. Within Europe, a
large consortium of academic and industrial partners
(EUROTAPES) has been collaborating to advance
in these demanding challenges. In this presentation,
several topics related to the recent progress in the
different aspects covered by the project will be presented
with emphasis on the solution chemistry approach
as a bottom-up strategy to reduce the figure of merit
cost / performance of the conductors. On one hand, I
will report on the efforts in increasing the robustness
of the ABAD coated conductor architecture and,
particularly, on the progress on using Ink Jet Printing to
produce multilayered structures with high total critical
currents. On the other hand, different approaches
related to achieving nanostructured superconductors
with enhanced flux pinning and high magnetic field
performances will be also presented. Particularly, a novel
path towards nanostructured coated conductors based
on colloidal solution precursors will be reported. The
YBCO nanocomposite films include BaZrO
3
or BaHfO
3
as second phase randomly distributed nanoparticles
within an epitaxial matrix. The correlation between
atomic scale defects, the nanoscale strain, evaluated
from X-ray diffraction line broadening and from HRTEM
and STEM, and vortex pinning efficiency at different
temperatures and magnetic fields will be analyzed.
Our work stresses that CSD is a bottom-up approach
with a strong potential to create cost-effectively coated
conductors with outstanding performances for a new
generation of magnets, motors and generators, fault
current limiters and cables.
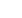
Figure:
Colloidal nanoparticles of BaZrO
3
prepared by
solution chemistry used to grow YBa
2
Cu
3
O
7
/BaZrO
3
superconducting nanocomposites.