allied
academies
MASS SPECTROMETRY
AND PROTEOMICS
International Conference on
J u n e 2 5 - 2 7 , 2 0 1 8 | D u b l i n , I r e l a n d
Journal of Systems Biology & Proteome Research
|
Volume 2
Page 31
Note:
S
mall thiolate-protected gold clusters have attracted considerable attention
as new functional nanomaterials because they have size-specific properties
and functions that are not found for bulk gold. In particular, hydrophilic thiolate-
protected gold clusters (hereinafter referred to as hydrophilic gold clusters)
exhibit high biocompatibility and luminescence quantum yield in addition to
pollution-free properties. Therefore, hydrophilic gold clusters are expected to
be used in biomedical and environmental applications. Replacing some of the
Au atoms in these clusters with different elements may impart them with even
more useful functions. However, the synthesis of hydrophilic metal clusters
has been less studied because of the complexity involved in evaluating the
mass distributions of product mixtures. In this work, we found two hydrophilic
interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) columns for high-performance
liquid chromatography (HPLC) suitable for the high-resolution separation of
hydrophilic metal clusters. The mass distributions of the product mixtures of
hydrophilic metal clusters were evaluated via HPLC mass spectrometry (LC/
MS) using these HILIC columns. Consequently, we observed multiple clusters
that had not been previously reported for glutathionate (SG)-protected gold
clusters (Au
n
(SG)
m
). Additionally, we demonstrated that Au
n−x
M
x
(SG)
m
alloy
clusters (M = Ag, Cu, or Pd) in which part of the Au in the Au
n
(SG)
m
cluster
is replaced by a heteroelement can be synthesized, similar to the case of
hydrophobic alloy clusters. It is easy to evaluate the mass distributions of
hydrophilic metal clusters using this method. Thus, remarkable progress in
the synthesis techniques of hydrophilic metal clusters through the use of this
method is anticipated, as is the situation for hydrophobic metal clusters.
Biography
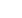
Yuichi Negishi received his Ph.D. degree in 2001
from Keio University, Japan. He is the professor
of Tokyo University of Science, Japan. He has
over 140 publications that have been cited over
7,200 times. In his publications, 10 papers are/
were categorized to Top 1% Cited Papers. His
publication H-index is 45. He has been awarded
several prizes, including the PCCP Prize (2007),
CSJ Award for Young Chemists (2008), Japan
Society of Molecular Science Award for Young
Chemists (2012), and Yagami Prize (2017).
negishi@rs.kagu.tus.ac.jpHIGH-PERFORMANCE LIQUID
CHROMATOGRAPHY MASS
SPECTROMETRY OF THIOLATE-
PROTECTED METAL CLUSTERS
Yuichi Negishi
Tokyo University of Science, Japanl
Yuichi Negishi, J Syst Biol Proteome Res 2018, Volume 2