allied
academies
Page 58
Journal of Industrial and Environmental Chemistry
|
Volume 2
GREEN CHEMISTRY &
TECHNOLOGY
7
th
International Conference on
J u n e 1 8 - 2 0 , 2 0 1 8 | D u b l i n , I r e l a n d
Xianwei Wang et al., J Ind Environ Chem 2018, Volume 2 | DOI: 10.4066/2591-7331-C1-003
IN SITU
MODULATION EXCITATION IR
SPECTROSCOPY IN ENVIRONMENTAL
CATALYSIS: NOX REMOVAL BY AU
CATALYSIS
Xianwei Wang
1
and
Nobutaka Maeda
1, 2
1
Dalian University of technology, China
2
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, China
O
ne of the greatest challenges for in situ characterization by Fourier
transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy for environmental catalysis
is to discriminate active species from spectator species dominating the
surface under steady-state reaction conditions. Hence, the selective
extraction of active species would be especially valuable for analyses
of heterogeneous catalysts. A transient spectroscopic technique,
modulation excitation spectroscopy (MES), was reported for the selective
discrimination by operating under an unsteady-state condition with a
periodic external perturbation, e.g. concentration. The phase sensitive
detection(PSD)wasadditionallyappliedtotransformtime-domainspectra
to phase-domain spectra1. Recently, we have applied this state-of-the-art
spectroscopic technique for NO reduction by CO over AuRh/TiO
2
nanowire
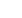
(NW) catalysts. Figure1shows insituMES-IRspectraunderNO-modulated
NO-CO reaction on AuRh/TiO
2
and AuRh/TiO
2
-NW. MES combined with
PSD increased the signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio, and time-resolution even in
the low absorbance range. Extraction of kinetic information of adsorbed
CO and NO on Au and Rh surfaces, isocyanate species (–NCO), hydrogen-
bonded OH and isolated OH on support materials were clearly displayed
in the phase-domain spectra. Negative NO bands (highlighted in blue)
in Figures 1a and 1b demonstrates the NO molecules adsorb differently
on TiO
2
and TiO
2
-NW. The phase-domain spectra (Figures 1c, 1d, 1e and
1f) display a dynamic
perspective on the
catalytic cycles:-NCO
formation on isolated
OH groups and its
reaction with NO to
produce final products,
i.e., N
2
and CO
2
. Figure
: (a, b) time- domain; (c,
d, e, f) phase-domain
spectra during periodic
change in the gas-
phase compositions
between NO + CO and NO over (a, c, e) AuRh/TiO
2
and (b, d, f) AuRh/
TiO
2
-NW catalysts.
Xianwei Wang is the PhD candidate in School
of Environmental Science & Technology, Dalian
University of Technology, China. He did his re-
search on Catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by
carbon monoxide. Synthesis and modification
of Au-based catalysts Application of in situ
modulation excitation infrared spectroscopy for
monitoring catalytic solid-gas and solid-liquid
interfaces and also the In situ ATR-IR Spectro-
scopic study of catalysts surfaces under high
pressure and temperature
wxwei@mail.dlut.edu.cnBIOGRAPHY