Page 14
allied
academies
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Toxicology | Volume: 3
February 21-22, 2019 | Paris, France
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology
International Conference on
M
etabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions including
hypertension, hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia with
central obesity. Present study was aimed to evaluate the
antihypertensive, antihyperlipidemic andantidiabeticpotential
of theselectedcompounds i.eBVAB-01/02usingrobustmodels.
Antihypertensive activity of test compounds was investigated
using DOCA-salt (Deoxycorticosterone acetate) induced
hypertensive rats. Antihyperlipidemic activity of compounds
was evaluated using triton X-100 and high fat diet induced
hyperlipidemia in rats. Antidiabetic potential of compounds
was screened using streptozotocin and high fat diet model in
rats. Oral administration of the test compounds (5 mg/kg and
10 mg/kg; BD) for six consecutive days produced significant
reduction in blood pressure inDOCA-salt (Deoxycorticosterone
acetate) induced hypertensive rat. Similarly, an impressive
reduction in serum lipid profile (cholesterol, triglycerides and
LDL) withmarked elevation of HDLwas recorded in triton X-100
and high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic rats. In antidiabetic
study, lowering of blood glucose level was evident only at high
dose in streptozotocin and high fat diet model. In addition, an
impressive reduction in coronary risk index and atherogenic
index was also recorded. In biochemical studies, treatment of
compounds resulted in the reduction of malondialdehyde and
nitric oxide with marked elevation of superoxide dismutase
and catalase enzymes level in liver, aorta and heart tissues.
Histopathological study of different organs namely heart, aorta
and liver clearly indicated protective roles of both compounds
in different model of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. In
conclusion, therapy with soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors
(BVAB-01/02) may produce encouraging outcomes in the
management of metabolic disorders. However, further study
is required to confirm their efficacy at clinical level.
Speaker Biography
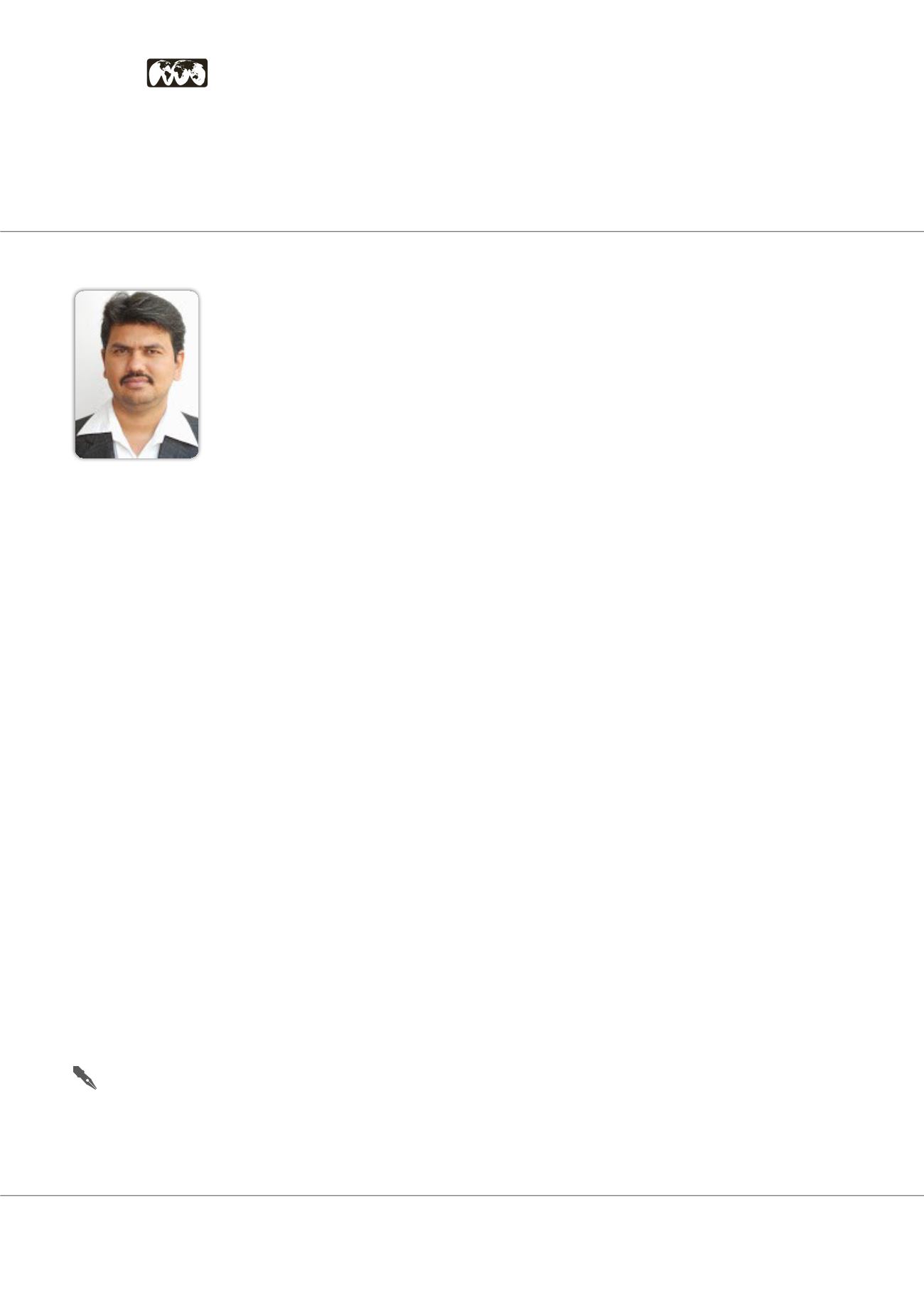
Swapnil Sharma is working in capacity of associate professor of Pharmacology, at Banasthali
University,
India.Heishavingmorethanthirteenyearsofexperience.Hiscoreresearcharea
includes cardiovascular pharmacology, neuropharmacology andmanagement of metabolic
diseases. He is having one Indian patent to his credit. He has published more than sixty
papers in journals of international repute. He is a reviewer of various peer review journals
to name a few; Life Sciences, Elsevier Publisher, Journal of Alternative and Springer etc. He
has also authored few books and chapters with good publishing houses. He has delivered
various lectures and has been recipient of various awards in national and international
conferences. He is also associated with various pharmaceutical bodies like APTI, IPA, STOX.
In addition, he is also acting as CPCSEA nominee to supervise animal experimentation at
different pharmacy institution in India.
e:
skspharmacology@gmail.comSwapnil Sharma
Akansha Bisht
Banasthali Vidhyapith, India
Promising role of novel soluble Epoxide Hydrolase inhibitors in management of
Metabolic Syndrome: A preclinical study
Notes:
Swapnil Sharma, J Clin Exp Tox, Volume 3
DOI: 10.4066/2630-4570-C1-004