allied
academies
Page 31
May 20-21, 2019 | Vienna, Austria
Biomaterials and Nanomaterials &
Materials Physics and Materials Science
2
nd
International Conference on
Journal of Materials Science and Nanotechnology | Volume 3
A heat capacitive PCB
Jonathan Silvano de Sousa, Maria Prutti, Bernd Schuscha
and
Qi Tao
Austria Technologie & Systemtechnik (AT&S AG), Austria
T
he paper describes a new concept for cooling electronic
applications where the heat capacity of the PCB is
enhanced. This is done by the utilization of commercial
phase change material (PCM) embedded in an epoxy resin
matrix in the PCB construction.
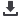
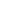
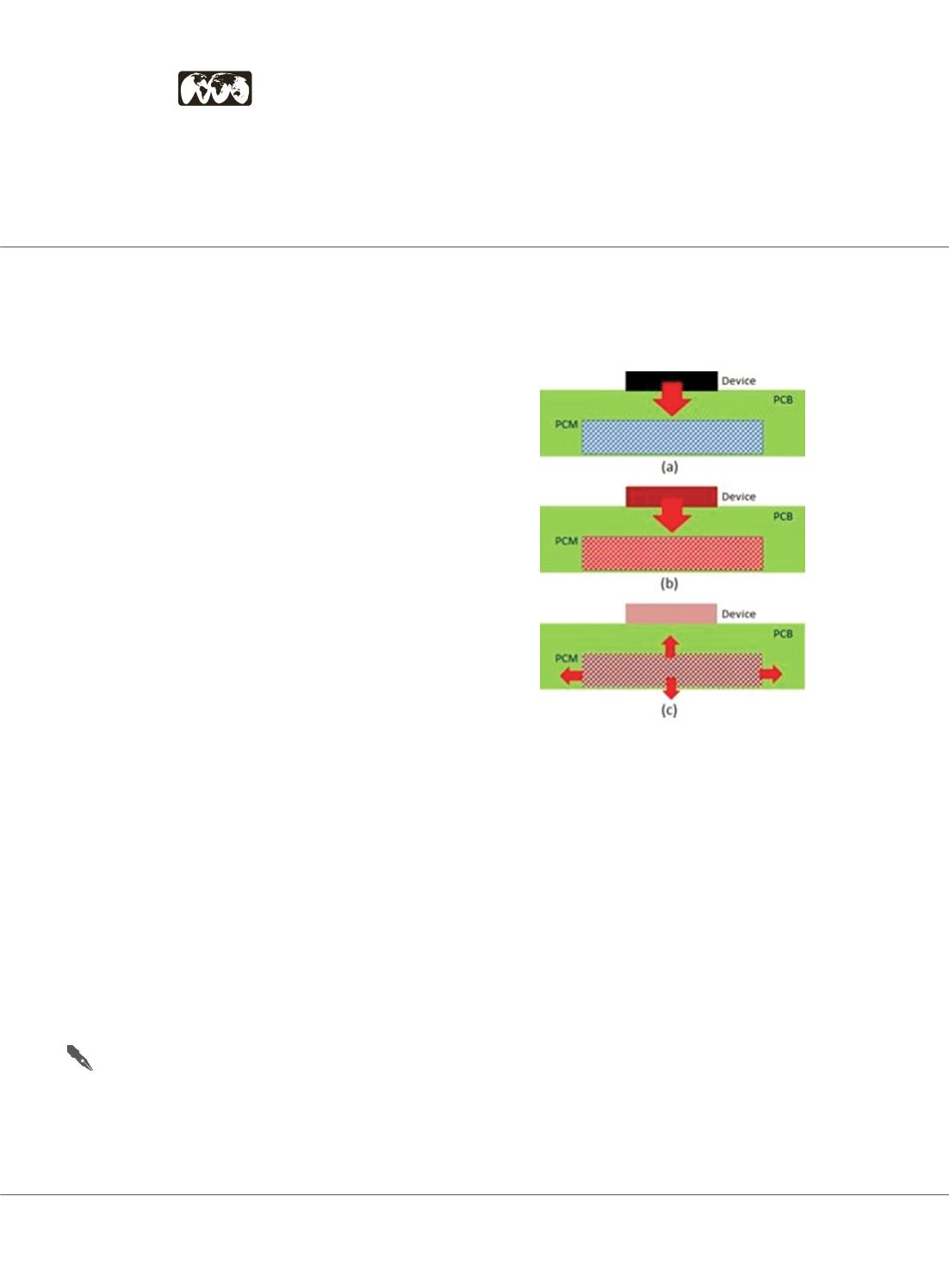
The basic idea of the concept is described in Fig.1 which
depicts the schematics of a PCB structurewith a component
(device) installed on its surface and a PCM epoxy matrix as
heat reservoir installed in its inner part (“a”). During phase
change, part of the dissipated heat is absorbed by the PCB
which results into a lower operational temperature for the
component and longer time for the system to reach steady
state (“b”). When the device is turned off, the stored
energy is released to the environment (“c”).
Benchmark measurements between conventional and
heat capacitive PCBs as well as basic reliability tests will be
shown. Further possibilities for technology development
and applications will also be discussed.
Speaker Biography
Jonathan Silvano de Sousa studied physics at the Technical University
of Vienna, Austria. He has extensive experience in the printed circuit
board and semiconductor industries. Since 2014, he has been heading
the research in heat management in the R&D department at AT&S.
e:
j.silvanodesousa@ats.netNotes:
Figure 1: Heat capacitive PCB