- Current Pediatric Research (2016) Volume 20, Issue 1
Screening for Hearing Loss among High Risk Neonates? Experience from A Tertiary Care Center.
- *Corresponding Author:
- B. Vishnu Bhat
Department of Neonatology, JIPMER, Pondicherry, India
E-mail: drvishnubhat@yahoo.com
| Date of Acceptance | April 18, 2016 |
Abstract
Early detection of hearing loss by screening and appropriate intervention is critical for development of speech, language and cognition. Indian data regarding screening for hearing loss among high risk neonates is limited and hence this study.
Material and methods: This descriptive study included all high risk neonates admitted to our tertiary care NICU over 2 years from January 2012 to December 2013. All the high risk neonates were evaluated with Transient evoked Otoacoustic emission (TEOAE). Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) was done at three months of age for those neonates who failed in the TEOAE screening. Infants with hearing loss were referred for detailed evaluation and appropriate rehabilitation.
Results:Out of 1537 high risk neonates, 5.9% had persistent failure with OAE test. Extreme low birth weight, extreme prematurity, mechanical ventilation and perinatal asphyxia were the predominant risk factors associated with hearing loss. OAE showed 92% specificity in comparison to AABR. Conclusion: OAE is safe and effective method of screening for hearing among high risk neonates.
Keywords
Neonates, hearing loss
Background
Hearing loss is one of the common congenital problems among neonates [1]. The prevalence of significant hearing loss ranges from 1.2 per 1,000 healthy newborn infants and 2 to 5% in high-risk newborns [2,3]. Nearly 50% of congenital hearing loss is due to genetic defects [1]. About 50% of hearing defects can be detected in a selective screening based exclusively on hearing risk criteria [1]. Early detection and intervention at younger age are critical for future speech, language and cognitive development. Neonates with congenital hearing loss should be identified within the first 3 months of life. However, the average age at detection is currently 24-30 months [4]. Hearing assessment can be done with either by Transient evoked Otoacoustic emission (TEOAE) or by Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR). Even though AABR is considered as the gold standard for hearing assessment, there are limitations for its routine use among newborns. Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs) are sounds of cochlear origin, which can be recorded by a microphone fitted into the ear canal. They are caused by the motion of the cochlea's sensory hair cells as they energetically respond to auditory stimulation. OAEs provide a simple, efficient and non-invasive objective indicator of healthy cochlear function. OAEs may be either spontaneous (SOAEs) or induced by acoustic stimulation (EOAEs). TEOAE is an effective method for neonatal audiological screening both in the general population and in high-risk infants [5]. Developed countries have universal newborn hearing screening protocols in place. However, Indian data regarding screening for hearing loss among high risk neonates is limited and hence this study.
Materials and Methods
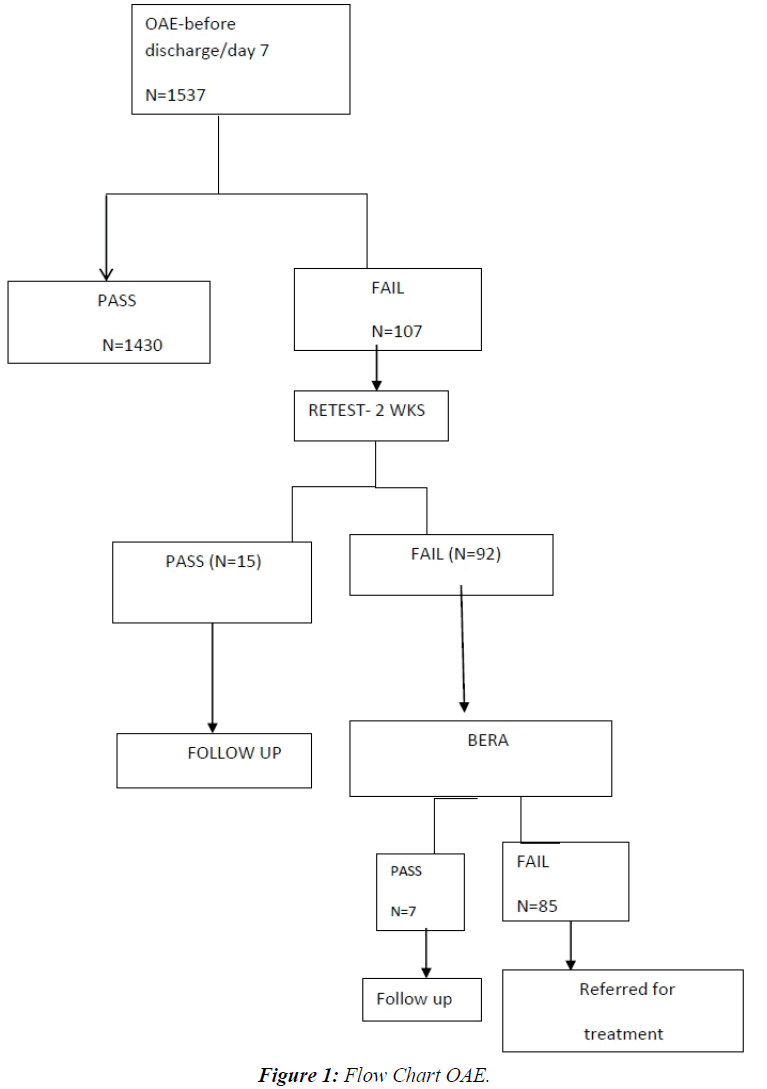
This descriptive study was conducted in our level III NICU of JIPMER, a tertiary care hospital in Pondicherry, India from January 2012 to December 2013 after due approval from the Institute Ethics Committee. The demographic parameters and important clinical details of all high risk neonates admitted during this period were collected. All intramural neonates with one or more of the following risk factors like family history of hearing loss, intrauterine infections, craniofacial malformations, hyperbilirubinemia, perinatal asphyxia, very low birth weight, sepsis, etc. were included in the study [6]. Babies with anotia were excluded from the study. The mothers were counseled regarding congenital hearing loss and the need for early diagnosis and intervention prior to the test. Written informed consent was obtained from the mothers. All these high risk neonates were evaluated with Transient evoked Otoacoustic emission (TEOAE) before discharge or day seven of life whichever was earlier. In case the baby failed, the test was administered again after two weeks. Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) was done at three months of age for those neonates who failed twice in the TEOAE screening. Infants with hearing loss were referred for detailed evaluation and appropriate rehabilitation. Normal hearing was defined on the basis of the presence and persistence of the V wave, for acoustic stimuli of 30dB. The infants with documented hearing defects (TEOAEs absent/V wave absent on AABR) underwent further evaluation and implementation of the sensorial activation programme. All these babies were followed up to six months. Results on categorical variables are presented as numbers and percentages (Figure 1).
Results
A total of 1537 high risk babies were screened for hearing loss. Persistent negative results with TEOAE were observed in 92 neonates (5.9%). Absent wave v was observed in 85 neonates. The TEOAE showed 92% specificity in comparison to AABR. False positive rate was 8%, which is acceptable clinically. On subgroup analysis hearing impairment was most common among extreme low birth weight babies. Mechanical ventilation and prematurity were also associated with increased hearing impairment. As the gestational age and birth weight reduced, the hearing impairment increased exponentially (Table 1).
| Risk factor | Number of neonates | Failed OAE-number (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Family history of hearing loss | 27 | 1 (3.7%) |
| Intrauterine infections | 189 | 7 (3.7%) |
| Birth weight 1250-1500 g | 637 | 21 (3.3%) |
| Birth weight 1000-1249 g | 356 | 27 (7.6%) |
| Birth weight 750-999 g | 107 | 18 (16.8%) |
| Gestation 27-28 wks. | 41 | 6 (12%) |
| Gestation 29-30 wks. | 70 | 7 (10%) |
| Gestation 31-32 wks. | 342 | 27 (8%) |
| Gestation 33-34 wks. | 440 | 22 (5.1%) |
| Craniofacial malformations | 34 | 3 (8.8%) |
| Hyperbilirubinaemia requiring exchange transfusion | 20 | 1 (5%) |
| Administration of ototoxic drugs >7 days | 317 | 7 (2.2%) |
| Meningitis | 90 | 8 (8.9%) |
| Apgar score<6 at 5 mt | 237 | 16 (6.8%) |
| Mechanical ventilation >5 days | 340 | 48 (14.1%) |
| PPHN | 51 | 2 (3.9%) |
Table 1: Risk factors and hearing impairment.
Discussion
Four to six out of every 1,000 children born in India have severe to profound hearing loss [2]. Hearing impairment has a devastating, detrimental and an invariably adverse impact on the development of newborns and psychological well-being of their families. According to the US Joint Committee on Infant Hearing position statement all the children must be screened for deafness by 1 month, diagnosed within 3 months and necessary intervention undertaken by as early as 6 months [7]. Our study confirms the accuracy of neonatal screening for congenital hearing loss using TEOAE, despite the fact that the possibility of false negatives (hearing neuropathy) must always be considered [8,9]. Extreme low birth weight, prematurity and mechanical ventilation were the major risk factors identified in our study. Possible explanations include cochlear immaturity in premature infants and middle ear with effusion secondary to prolonged tracheal intubation [10]. The low frequency of TEOAEs detectable in the high-risk sub population is similar to observations in other earlier studies [11-13]. The results stress the importance of identifying risk factors like prolonged assisted ventilation, extreme prematurity and severe birth asphyxia. The prevalence of congenital hearing loss is fifty times higher in the high-risk sub population compared to the normal population [2]. The study also confirms the feasibility of universal screening for congenital hearing loss. There are disadvantages of using TEOAEs for newborn screening [13-15]. TEOAE failure is higher during the first 24 hours of life due to debris in the ear canal or fluid behind the tympanic membrane. The fail rate is higher with OAEs (7 to 10%) than AABR (less than 2 to 4%) due to the sensitivity of OAEs to outer and middle ear problems [16-18]. This false positivity can be reduced by a delayed test as in our study. The fitting of the small probe must have a tight seal and requires expertise. Environmental and physiologic low frequency noise will increase the failure rate. Using separate sound proof room improves the specificity.
Our study showed a higher rate of positivity compared to the study done by Prieve et al. (less than 1%) [10]. John et al., noted prematurity as the most common risk factor among high risk babies, i.e. 26 (56.5%) out of 46 extremely preterm babies [11]. Chan et al. have shown 6.47% hearing impaired babies among 309 high risk babies screened [14]. In our study 6% hearing impaired babies were identified out of 1537 high risk babies screened, which is similar to that of Chan et al. and John et al. had showed that refer rate of initial test of 6.4% which reduced to 1.6% on subsequent tests [11,14]. With each retest, the positive predictive value of OAE increases and children with true deafness are identified [19-21]. TEOAE can be done easily by the bedside and sedation is not needed. Problem with TEOAE screening is that the environment should be silent which may not be possible inside the NICU. So there should be a separate audiology room near the neonatal intensive care. Another problem with early screening is the false negative results caused by the vernix in the external auditory meatus [22-24]. Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry (BERA), though highly reliable, requires more technical expertise, sedation and is also expensive. Time required for BERA test may not be tolerated by the sick newborn [25,26].
Conclusion
TEOAE can be effectively used for hearing screening of high risk newborns. Prematurity, low birth weight, mechanical ventilation and perinatal asphyxia are significantly associated with hearing impairment.
References
- Tucci DL, Merson MH, Wilson BS. A summary of the literature on global hearing impairment: current status and priorities for action. OtolNeurotol 2010; 31:31–41.
- Nagapoornima P, Ramesh A, Srilakshmi, et al.Universal hearing screening. Indian J Pediatr 2007;74:545–549.
- Paul AK. Early identification of hearing loss and centralized newborn hearing screening facility—the Cochin experience. Indian Pediatr 2011; 48:355–359.
- Mangla S, Kaushal R. Importance of new born hearing screening. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2009;61:157–159.
- Biswas A. Clinical audio-vestibulometry for otologists and neurologists, Assessing the deaf child, 3rd edn. Bhalani Publishing House, Mumbai,2007: 97-99.
- Report of collective study on prevention and etiology of hearing impairment.ICMR and Department of Science, New Delhi 1983.
- Joint committee on Infant Hearing. Position statement; Principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics 2000;106:798–817
- Harvey C. New born hearing screening. AustPrescr 2003;26:82-87
- Margaret AK. Neonatal hearing screening. PediatrClin N Am 2003;50:301–313
- 10) Probst R, Lonsbury-martin BL, Martin GK. A review of otoacoustic emissions. J AcoustSoc Am 1991; 89:2027-2067.
- John M, Balraj A, Kurien M. Neonatal screening for hearing loss: pilot study from a tertiary care centre. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2009; 61:33–36.
- Salamy A, Eldredge L, Sweetow R. Transient evoked otoacoustic emissions: feasibility in the nursery. Ear Hear 1996; 17:42-48.
- Downs SM, Kemper A. A cost-effectiveness analysis of new born hearing screening strategies. Arch PediatrAdolesc Med 2000;154:484–488
- Chan KY, Lee F, Chow CB, et al. Early screening and identification of deafness of high risk neonates. J Paediatr1998;3:131–135
- Mehl AL, Thomson V. Newborn hearing screening: the great omission. Pediatrics 1998;101:1–6.
- Sorenson P. Universal hearing screening in the NICU: the Loma Linda University Children’s Hospital experience. Neonatal Netw 1998;17:43-48.
- Hall JW. Otoacoustic emission facts and fantecies. The hearing journal 1992;45:7-45
- National Institutes of Health. Early identification of hearing impairment in infants and young Children. Consensus Development Conference on Early Identification of hearing lossin Infants and Young Children. Bethesda, MD. NIH Consensus Statement 1993; 11:1-24.
- Stein LK. Factors influencing the efficacy of universal newborn hearing screening.PediatrClin North Am 1999;46:95-105.
- Lutman ME, Grandori F. Screening for neonatal hearing defects. European consensus statement. Eur J Pediatr 1999;158:95-96.
- Kemp DT. Stimulated acoustic emissions from within the human auditory system. J AcoustSoc Am 1978;64:1386-1391.
- Rasmussen AN, Osterhammel PA, Johannesen PT, et al. Neonatal hearing screening using otoacoustic emissions elicited by maximum length sequences. Br J Audiol 1998;32:355-366.
- Vinck BM, Van Cauwenberge PB, Corthals P, et al. Multi-variant analysis of otoacoustic emissions and estimation of hearing thresholds: transient evoked otoacousticemissions. Audiology 1998; 37:315-334.
- Hatzopoulos S, Petruccelli J, Pelosi G, et al. TEOAE screening protocol based on linear click stimuli: performance and scoring criteria. ActaOtolaryngol 1999;119:135-139.
- Kakigi A, Hirakawa H, Hare N, et al. Comparison of distortion - product and transient evoked otoacoustic emissions with ABR threshold shift with ototoxic damage. AurisNasus Larynx1998; 25:223-232.
- Ochi A, Yasuhara A, Kobayashi Y. Comparison of distortion product otoacoustic emissions with auditory brainstem response for clinical use in neonatal intensive care unit ElectroencephalogrClinNeuropathol 1998;108:577-579.