Review Article - Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences (2020) Volume 10, Issue 70
Review on comprehensive understanding of building an analytical quality by design for drug manufacturing process.
Shishir Kumar Prasad*, Kalpana Diwekar, Anita A
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Dayananda Sagar University, Bangalore 560078, India
- Corresponding Author:
- Shishir Kumar Prasad
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Dayananda Sagar University
Bangalore, India
E-mail: anita19965@gmail.com
Accepted date: April 10, 2020
DOI: 10.35841/2249-622X.70.8911
Visit for more related articles at Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical SciencesAbstract
When knowledge based on pure scientific understanding and quality risk management is applied to
product and process learning with regulation on process control along with a systematic approach for
development of predefined objectives in analytical field then it is called as quality by design or QBD it
follow ICH guidelines for quality in pharmaceutical product concept of QBD also extends to analytical
methods, it is mandatory process in QBD to define a goal.
A protocol for the method which will continue monitoring the process throughout in a systematic way
and working on alternate methods as well to get optimal performance, the methods given are carefully
analyzed in structured pattern for risks and is put for a challenge of the validity of method which later
on can be taken for the criteria, benefit of these studies.
The performances can be improved as well as clearly understood along with the risk management and
desired performance methods which can also be validated later on, the review briefly gives an inside
view of application of analytical QBD in industries and its current status with examples and principles
of analytical methods in HPTLC ,titration for moisture content, determination of toxic impurities in
mixtures, quantative colour measurement and various spectroscopic method for identification of
chemical moiety.
QBD developed spectroscopic and chromatographic method is usually done as per ICH Q8 R2, the
critical parameters are compared to principle observation and analysis, the HPTLC method employs
solvent usage and detection of absorbance and wavelength comparison.
Keywords
HPTLC, Toxic impurities, Analytical target, Design formulation.
Introduction
As science is now based on quality management system, with quality to be built in QBD aims into looking into the quality of analytical process during development stage itself instead of waiting for final result for an integrated approach to development manufacturing and quality for both industry and regulators [1]. As per FDA guidelines for process validation at three step approach can be utilized (Figure 1).
Stage 1: Design of ATP {analytical target profile} the method and conditions required to control critical values
Stage 2: Qualification: the methods utilized is capable of its purpose
Stage 3: Continuous monitoring: the methods utilized are ensured to remain in monitoring for intended work
Various Elements of QBD
Product and process design and development [2], the products are identified as per critical quality assessments and it is up fronted for the desired performance. The design formulation and process are made to meet the product specific requirement. Risk assessment and risk control it includes the impact of material testing to be clearly understood, product eqas and process parameter with various attributes are explained well. The identification and control of variability in process and material management is followed, To assure the consistent quality all the process are continuously monitored and updated (Table 1).
| Traditional approach | QBD |
|---|---|
| Product develpoment | Product development |
| Fixed batch manufacturing process | Responsive batch or continuous |
| Fixed batch packagig process | Manufacturing process |
| Product quarintine | Reponsive pkg process |
| Product disrtibution | Product distribution |
| Fixed parameters ranges | Design- control dtrategy |
| In-process testing process | Real Time Release |
| Documentation |
Table 1: System comparision of pharmacuetical supply and analytical system.
Quality target product profile
The perfect quality of a drug is ensured by all the acceptable control strategy and all the process with and formulation which are quite robust of the results. Critical quality attributes: A CQA is a characteristics that should be within an appropriate limit, range or distribution which can have physical, chemical biological or microbial property range or distribution to ensure the desire product quality as per the guidelines (ICH Q8 R2) CQ As which are generally associated with drug substance, intermediates, in processes, final products and excipients as well [3-7].
Quality risk managements
Q9 Describes systematic approach for assessment control communication review, it even applies for product lifecycle development manufacturing and distributions, it is also inclusive of principle methodologies and examples of tools for risk quality management and assessment of risk to quality should be linked to protection of patients based on scientific knowledge, and extend over the life cycle of the a pharmaceutical product [4].
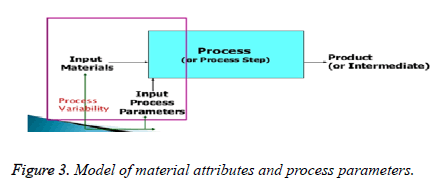
Process parameters
A process parameters whose viability has an impact on a critical quality attribute and therefore should be monitored or controlled to ensure the process the desired quality (Q8 R2), cppc have a direct impact on CQAs, The examples in temperature, pH, agitation, dissolved ratte of oxygen are all measured parameters which can be easily adjusted which are controlled as well are measured parameters [9-12].
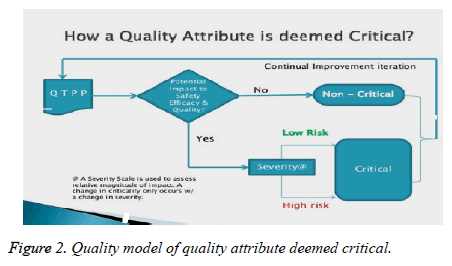
Quality Attribute Deemed Critical
A severity scale is used to assess relative magnitude of impact. A change is critical only when it is in severity (Figures 2 and 3).
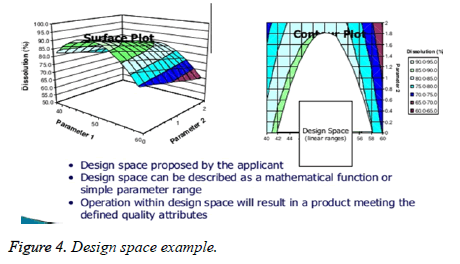
Design space approach
First principle approach is combination of experimental data and mechanical knowledge of chemistry physics and engineering to model and predict performance, next is non-mechanistic or empirical approach statistically designed experiments (DOES),along with linear and multiple linear regression, after that comes the scale up co-correlations which translates the operating condition between different scales or pieces of equipment’s, all steps are culminated into risk analysis which determines the significance of effects and any combination of above (Figure 4).
Continuous improvement of various process and the product
Various processes like manufacturing, performance, monitoring ,market variance are made to acceptable changes by continuous improvement to increase the product lifecycle with regular feedbacks which is the basis of expanded knowledge and results in management with original concept intact [9-20].
Conclusion
QBD is the developmental approach which should be adapted based on the complexity and specificity of product and design, FDA encourages these practices to be include in their application by the industry, using QBD does not bring about any change in the regional regulatory process but provides more of scientifically proven flexible approaches to them and for which in any case the adherence to GMP is any required. Various process like inspections and reviews, and the flexible regulatory approaches to facilitate these does prove that, opportunity does existto develop more appropriately factors depending on the level of understanding achieved and adapted quality system in place, the approved design space described within the manufacturing process movements without further regulatory views, with a reduction of post approval submissions, and a real time release testing leading to reduction of end product release testing.
References
- CON ICH Topic Q8 (R2). ICH harmonised tripartite guideline.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH '09), Pharmaceutical Development. 2009.
- Godfrey AB,Kenett RS, Juran JM.APerspective on Past Contributions and Future Impact. Quality RelEngInternat. 2007; 6: 653–663,
- Nethercote P, Borman P, Bennett T, et al. QbD for Better Method Validation & Transfer,PharmaceuticalManufacturing. 2010.
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) ofTechnical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuti-cal for Human Use, Topic Q8 (R2): Pharmaceutical Development, Geneva, 2009.
- Vemuri P, Kumar N, Gupta V. A Review on quality bydesign approach (QBD) for Pharmaceuticals. IntJ drug deve Res. 2011; 7: 1.
- Khamanga SM, Walker RB. The use of experimental design in the development of an HPLC-ECD method for the analysis of captopril. Talanta.2011; 83: 1037–1049
- Sheldon EM,Downar JB. Development and validation of a single robust HPLC method for the characterization of a pharmaceutical starting material and impurities from three suppliers using three separate synthetic routes. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal.2000; 23: 561–572.
- Gavin PF, Olsen BA. A quality by design approach to impurity method development for atomoxetine hydrochloride (LY139603). JPharmaceut Biomed Anal. 2008; 46: 431–441.
- ICH Topic Q2 (R1). ICH harmonised tripartite guideline.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH '94). Validation of Analytical Procedures, 1994.
- ICH Topic Q9. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH '94). Quality Risk Management, 2005.
- Borman P, Nethercote P, Chatfield M, et al. The Application of Quality by Design to Analytical Methods. Pharm Tech. 2007.
- Yu LX. Pharmaceutical quality by design: product and process development, understanding, and control.PharmaceutRes.2008: 25: 781–791.
- Pohl M, Schweitzer M, Hansen G, et al.Implications and opportunities of applying the principles of QbD to analytical measurements. Pharmaceut Tech Europe. 2010; 22: 29–36.
- The United States Pharmacopoeia 27, the National Formulary 22, Asian Edition, United States Pharmacopoeial Convection, 2004.
- Vikas PM, Satyanarayana DT, Kumar DV, et al. Development and validation of new RP-HPLC method for the determination of Sofosbuvir in pure form. WorJ PharmPharmaceutSci 2016.
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) Q11: Development and Manufacture of Drug Substances (Chemical Entities and Biotechnological/Biological Entities). 2011.
- Schweitzer M, Pohl M. Hanna BM, et al. Implications and Opportunities of Applying QbD Principles to Analytical Measurements. Pharm Tech. 2010; 34: 52-59.
- Vogt FG, Kord AS. Development of Quality-By-Design Analytical Methods. J Pharm Sci. 2011; 100: 797-812.
- Bhatt DA. Rane SI. QbD Approach to Analytical RP-HPLC Method Development and its Validation. Int J PharmPharmaceut Sci. 2011; 3: 180-187.
- Borman P, Nethercote P, Chatfield M, et al. The Application of Quality by Design to Analytical Methods. Pharm Tech. 2007.