Review Article - Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences (2020) Volume 10, Issue 70
Pros and Challenges to Pharmacists in Prescribing Practice.
Majid Khan*
Department of Pharmacy, Shaheed Benazir Bhutto University Sheringal Dir Upper Khyber Pakhtun, Khwa, Pakistan.
- Corresponding Author:
- Majid Khan
Department of Pharmacy Shaheed Benazir Bhutto
University Sheringal Dir Upper Khyber Pakhtun Khwa
Pakistan
E-mail: majidkhanpiran@gmail.com
Accepted date: April 17, 2020
DOI: 10.35841/2249-622X.70.7832
Visit for more related articles at Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical SciencesAbstract
Pharmacists are the hearts of health care team and independent prescribers in United Kingdom and other developed countries. Nowadays pharmacists oriented to patient care rather traditional mercantile products orientation. Clinical Pharmacy is the combined agreement between physician and pharmacist in which pharmacist prescribing and providing patient care. The health care team is fragile in the absence of pharmacist, literature supported prescription by pharmacists and the members include physicians, stakeholders and patients, but some physicians not supported them due to loss of dignity, deskilled junior physicians and some considered them deficient of well diagnostic skills. Provision of drug therapy without competent clinical pharmacist is impossible and incomplete. The implementation of pharmacists prescribing can effectively decrease burdens and workload from the shoulders of physicians to provide them time for complex diseases, facilitate pharmacists regarding jobs issues instead of five years degree of Doctor of Pharmacy, patient counseling and educations, reduction of polypharmacy and iatrogenic diseases as well as to stabilize the health care triangle.
Keywords
Clinical Pharmacy, Clinical Pharmacists, prescribing pharmacists, health care triangle
Introduction
World prescribing practice by Pharmacists introduced in 1970-80s due to development of clinical pharmacy modifying patient condition in 1960 [1]. The liaison between physician and pharmacist of many decades from Greek time where “Asclepius” was the physician he chooses and worked with a girl Pharmacist “Hygeia”, in this time she was called Apothecary the new name is Pharmacist, this indicates the relation of Pharmacist with Physician.
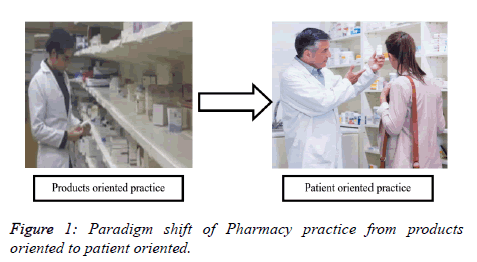
Pharmacists are nowadays independent, non-medical, health team prescribers in United Kingdom [2]. This due to advance practices Clinical Pharmacy which is the liaison of pharmacist with physician in which pharmacists prescribing [3]. Nowadays the pharmacy profession upgraded via paradigm shift from product oriented practice to patient oriented this is also called Pharmaceutical care [1-4]. The transform of mercantile practice of pharmacists into clinical one but some barriers shows hindrance like problem in educational standard, skills and practical environments [5]. Clinical Pharmacy has expanded the roles of pharmacists globally from traditional dispensing practice to pharmaceutical care and direct patient involvement and staff consultation [6] (Figure 1).
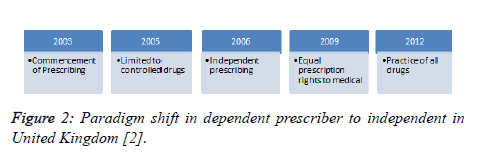
The prescribing practice of pharmacists started with alternate barriers of controlled and schedule drugs with years changes the practice to independent practice [1]. In 2003 prescription practice by pharmacists commenced but were limited drugs and dependent practice after physician diagnose, in 2005 permitted them to prescribe even controlled drugs in 2006 the dependent prescription practice converted into independent one and in 2009 legislative changes convert them into independent prescriber with equal rights to medical prescribers, in early 2012 with amendment in rules eliminated the limitations of controlled drugs but practice limited to schedule drugs, after that independent pharmacists practice mostly in cardiovascular system, central nervous system, endocrine, total parenteral nutrition management and many more as per their competency initiated by pharmacists with legal authorities to prescribe every drug to every patient [2] (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Paradigm shift in dependent prescriber to independent in United Kingdom [2].
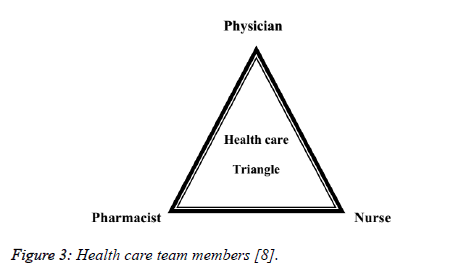
Changes in legislation allowed pharmacists to work independent prescribers created more opportunities for pharmacists to work along with medical team members in health care triangle [7] (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Health care team members [8].
The prescribing pharmacists prescribed as per the standard guidelines like World Health Organization, British National Formulary and others thus decreased the burdens and workload from the shoulders of physicians [2]. The respondents also satisfied from these prescribers. A great revolution in the prescription of Pharmacists from dependent, limited drugs to independent unlimited and every drug to every patient, the relationship between Pharmacist, Physician and nurse existed in triangle and every angle of triangle has their own importance, thus with the absence of any of them the health care team is incomplete [7,9].
Discussion
Study conducted in Scotland by Dereck C. Stewart et al 2009, regarding pharmacists prescribing comments from physicians, pharmacists, patients and stakeholders in which all were strongly agreed only physicians were not agreed up to the marked level due to boundary encroachment, insufficient diagnostic expertise and deskilling junior physicians [1,10]. Some physicians also reported positive comments on prescribing of pharmacists due to review of comprehensive medications [1]. On other hand experts and patients presented that pharmacists are experts in medications, therapeutic drugs monitoring, pharmacoeconomics and patient counseling. From prescribing the pharmacists were autonomous with job satisfaction considered responsible and strong liaison in health care team [10].
Literature showed that pharmacists prescribing can effectively reduced pain related issues [1] by adopting World Health Organization like prescription indicator, facility and patient care indicator as well as “three steps analgesic ladder” [11].
Auta et al. 2015 articulated that the prescribing pharmacists can effectively decreased and utilized 10 hours weekly from 58 hours to 48 hours of physicians in order to freeing them for complex cases, decreased workload from the shoulders of physicians also increase team work this studies also indicates that almost 2400 independent pharmacists prescribing in United Kingdom [1]. Published data purports the patients views about the hypertension in uni-clinic where better standard patient care provided by Pharmacists than before [10].
Graziano et al. 2013 articulated that Pharmacists can effectively decrease the medication errors in absence of Pharmacists were 95% and decrease to 47% in hiring Pharmacists in hospital. They implemented pharmacists in health care team [12]. World Health Organization documented that 50% patients fail to take correct therapy due to lack of awareness about their medications and remaining half is due to medication errors thus net zero therapeutic effect [13,14].
Pharmacist’s consultations can effectively decrease iatrogenic diseases and polypharmacy [15]. Ahmad et al 2018, insists the presence of pharmacists round the clock with full day and night duty in order to effectively reduce patients complaints and provide health efficiently [16].
In Ethiopia study conducted by Berha et al 2018 of 2000 patients, in which they found extensive prescription errors and recommended the presence of clinical pharmacists to improve the rational World Health Organization recommended therapy. They also focused on pharmacists orientations to patient care rather old traditional products and mercantile oriented practice [6,9,17].
Conclusion
Health care team is fragile in the absence of pharmacist, literature supported prescription by pharmacists and the members include physicians, stakeholders and patients but some physicians not supported them due to loss of dignity and some considered them deficient of well diagnostic skills. Provision of drug therapy without competent clinical pharmacist is impossible and incomplete. The implementation of pharmacists prescribing can effectively decrease burdens from shoulders of physicians to provide them time for complex diseases, facilitate pharmacists regarding job issue instead of five years degree of Doctor of Pharmacy, patient counseling and educations, reduction of polypharmacy and iatrogenic diseases as well as to stabilize the health care triangle.
Conflict of Interest
Nil
References
- Auta A, Strickland HB, Maz J, et al. Pharmacists prescribing in the United Kingdom and the implication for the Nigerian context. West Afr J Pharma. 2015; 26: 54-61.
- Baqir W, Miller D, Richardson G. A brief history of Pharmacist Prescribing in the United Kingdom: Draft, country focus. Europ J Hosp Pharma. 2012; 9.
- Amir M. Clinical Pharmacy Practice: An activity based definition for Pharmacy students of developing countries Arch Pharma. 2012; 3.
- Khattak S, Ahmad T, Ullah A, et al. Evaluation of Prescription Errors at Health care system in Khyber Pakhtun Khwa (KPK). Pak IJBMSP 2017; 7.
- Maqbool M, Clinical Pharmacy Practice in Health care system: A review. Eur J Pharma and Med Res. 2019; 6: 630-633.
- Mekonnen AB , Yesuf EA, Odegard PS, et al. Pharmacists journey to clinical Pharmacy practice in Ethiopia: Key informants perspective. SAGE open medicine 2013.
- Adnan S. The role and scope of pharmacists in community settings: A review of developing countries International J Allie Med Sci and Clin Res. 2014; 2: 32-35.
- Khan M. Role and Structure of Pharmacy and Therapeutic Committee concern to Pharmacist: Short Review. Pharma Qual Assu and Qual Cont. 2020; 1: 31–34.
- Aslam N , Zafar K. Ahmed Clinical Pharmacy Clerkship in Pakistan: A leap from paper to practice. Inno in Pharma . 2011; 2: 1-4.
- Stewart DC. Views of pharmacist prescribers, doctors and patients on pharmacist prescribing implementation. Int J Pharma prac IJPP. 2009; 17: 89-94.
- WHO, Promoting rational use of medicines: core components, World Health Organization Geneva. 2002.
- Onder G. Strategies to reduce the risk of iatrogenic illness in complex older adults Oxford University press on the behalf of British Geriatrics Society 2013; 42: 284-91.
- Peer RF, Shabir N, Iatrogenesis: A review on nature, extent, and distribution of healthcare hazards. J Family Med Prim Care. 2018; 7: 309-14.
- WHO, World Health Organization WHO patient safety Research topic, better knowledge for safer care, 2009.
- Permpongkosol S, Iatrogenic disease in the elderly: risk factors, consequences and prevention Clin interve in Ag Dovepress. 2011; 77-82.
- Ahmed T, Haq N, Ammar M, et al. Assessment of Inpatients Omission Errors Made by Nurses Through The Med Adminis Proc, MOJ Toxi. 2018; 4: 242-245
- Berha ABSN. Evaluation of drug prescription pattern using the World Health Organization prescribing indicators in Tikur Anbessa Specialized hospital. J drug del Therap. 2018; 8: 74-80.