Research Article - Journal of Clinical Ophthalmology (2022) Volume 6, Issue 3
Optometry in crime scene investigation
1Department of Optometry, Chandigarh University, Mohali, Punjab, India
2Department of Forensic Science, Chandigarh University, Mohali, Punjab, India
- Corresponding Author:
- Raj Kumar
Department of Optometry
Chandigarh University
Mohali
Punjab
India
E-mail: optomrajlvpei@gmail.com
Received: 31-May-2022, Manuscript No. AACOVS-22-65476; Editor assigned: 02-Jun-2022, AACOVS-22-65476 (PQ); Reviewed: 16-Jun-2022, QC No. AACOVS-22-65476; Revised: 01-Aug-2022, Manuscript No. AACOVS-22-65476); Published: 08-Aug-2022, DOI: 10.35841/AACOVS.6.3.1-4.
Citation: Kumar R, Kaur A. Optometry in crime scene investigation. J Clin Ophthalmol. 2022;6(3):1-4.
Abstract
Biological fluids such as blood, saliva, urine, semen, vaginal secretions etc. carry a great evidentiary value when found at the crime scene. But due to lack of awareness in case of tears. The presence of tears at the crime scene reflects that the person was emotionally disturbed such as in the case of kidnapping, physical torture, suicide/murder, etc. Therefore the ophthalmic evidence such as spectacles, contact lenses, etc. strengthens the evidentiary value. Forensic optometry is yet to get streamlined along with the routinely followed investigative techniques and scientifically explored although no standard protocols exist to analyze eyewear.
Keywords
Tears, Biological fluids, Saliva, Investigation, Crime scene, Physical torture.
Introduction
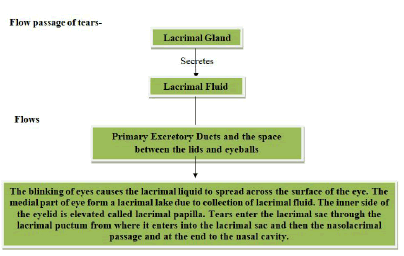
Composition of Tears: The lachrymal glands present in the eyes secrete a transparent liquid called tear. Tears can be differentiated into 3 layers i.e. lipid, aqueous, mucous [1]. The composition of tears includes water, antibodies, salts, antibacterial enzymes. Adrenocorticotropic hormone and leucine enkephalin are the stress hormones that are present in higher concentration in emotional tears (Table 1).
Table 1. Composition of tears and their functions.
| S. No. | Layer | Content | Secretors | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lipid | Contains Oil | Secreted by the tarsal glands. | The lipid layer provides a hydrophobic barrier that coats the aqueous layer. |
| 2 | Aqueous | Contains 60 metabolites and Electrolytes. | Secreted by lacrimal glands. | It controls the osmotic regulation and also the infectious agents. |
| 3 | Mucous | Contains Mucin (have ability to form gels). | Secreted by conjunctival goblet cells. | It provides a hydrophilic layer and coats the cornea. |
Table 2. Types of tears and their description.
| S. No. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basal | For the lubrication of the cornea small quantities of tears are released continuously. They fight against infectious agents such as viruses, bacteria, etc. and are also considered a part of our immune system. These are also called basic functional tears because they ensure comfort and good visual acuity. |
| 2 | Reflex | They are also known as Irritation tears because they are the result of the irritation caused in the eyes due to the foreign particles. They can also occur due to bright light. They are produced in higher quantities than the basal tears but the goals are the same. |
| 3 | Emotional | Also called Psychic tears, crying, etc. These result from strong emotions such as sorrow, anger, happiness, etc. |
Prospects of tear examination: Biological body fluids play an important role in personal identification such as blood, saliva, semen, tear, etc. Tears are exposed to both the internal and external environment; possess the significant value in determining the molecular information to diagnose ocular diseases (Figure 1).
Materials and Methods
Sample collection and storage of tear
During crime scene investigation, tear samples can be present on the tissue papers, bed sheet, and handkerchief. The body fluids possess the property of fluorescence when they are examined under the light of different wavelengths. A tear sample is collected from the subject’s conjunctival sac of the eye in a small glass capillary tube [2].
Direct sampling method: In 2013, Kalsow, et al. worked on the tear cytokine response to multipurpose solution for contact lenses. Before the lens removal, from the inferior tear meniscus non stimulated tears were collected from both eyes with the help of 10 microliter flame polished glass micropipette [3]. Then, immediately 5.5 microliters of the tear is transferred to a sterile. 0.2 ml tube which contains 49.5 microliter storage mixture at -80°C.
Indirect sampling method: Pre-Corneal Tear Film (PCTF) is collected with the help of Schirmer’s test strip, other absorbing materials such as cellulose sponge, filter paper, etc.
ELISA: Enzyme Linked Immune Sorbent Assay (ELISA) technique is used to analyze inflammatory markers in PCTF. A weak cell sponge is used to collect 10 microliters of tears [4]. The concentrations of Interleukin (IL), IL-6 and pro-MMP-9 were measured by Enzyme-Linked Immune-Sorbent Assay check (ELISA), and the MMP-9 activity was evaluated with gelatin zonography.
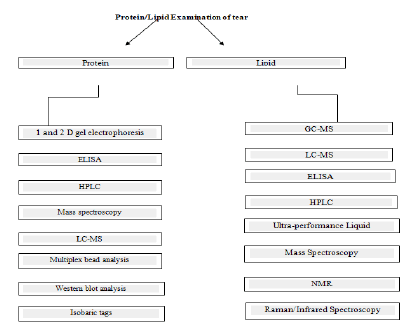
Luminex technology: To quantify the cytokine profile ophthalmic sponges and extraction buffer are compared using Luminex technology. Merocel sponge is used to collect the cytokine profiles of tears (Figure 2) [5].
Results and Discussion
Table 3. Past few year studies by authors on the collection method of tear (Studies were performed on humans).
| Reference | Status of Individual | Analytical Sample | Sample Obtaining method | Sample Volume | Pros and Cons | Biochemical Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kalsow et al. | Contact lens Users | Cytokines | Non stimulated tears gathered with help of 10 microliters glass micropipette. | -5.5 microliters | It is a viable method for the examination of cytokine with cytokine assay | Multiplex cytokine bead assay |
| Guyette et al. | ADDE and non-ADDE Patients | Low-level abundance biomarkers | NST and WO collected with help of 10 microliters glass micropipette. | Min.6.5 microliters | The WO tears do not give accurate conc. of cytokine in elevated NST | Multiplex cytokine bead assay, PCR. |
| Green-Church et al. | Healthy Individual | Tear Protein | Schirmer’s strips and glass micro capillary pipe. | Min. 5l L, 3-16 pooled samples non Determinable, Schirmer’s strips were place into 100 L buffer. |
From the Schirmer’s strip, it is difficult to find out protein concentration. | SDS-PAGE, 2D-SDS PAGE, and 2D LC-MS/MS multidimensional protein identification technology. |
| Acera et al. | Ocular surface disease patients | Inflammatory cytokines | Ophthalmic sponge | 10 microliters | Only justified for IL-Beta, IL-6, and MMP-9 | ELISA |
| Inic Kanada et al. | Healthy Individuals | Cytokine | Different ophthalmic Sponges such as Merocel, pro-ophta, etc. | Non-defined | Ophthalmic sponges are well Bear by the patient, Particularly children. |
Multiplex cytokine bead assay |
| Lee et al. Satpathy et al. |
Person suffering from Herpes virus keratitis. |
Herpes Simplex Virus I | Schirmer’s strips WO (accumulated with glass capillary micropipette). |
10 microliters | Non-dependent on tear collection method. | PCR |
Significance of tear in personal identification: The process of investigation involves the identification of the suspect/criminal [6-8]. Therefore a subject to objective approach is followed by the forensic laboratories (Table 3). DNA Technology is used for the identification of known/unknown individuals in the cases such as genealogy studies [9,10], maternity/paternity testing. The use of tear along with the eyewear examination can strengthen the ease of identification (Table 4). They are secreted in small (Figure 2) quantities and are found in a dried state which can be diagnosed using presumptive test and can be confirmed using the confirmatory test.
Table 4. Result of extraction from tear/Optical evidence found on the crime scene.
| Reference | Extraction from tear/optical evidence found on the crime scene | Analysis/result |
|---|---|---|
| Marshall S, Rodrigues A, and Hird HJ.(2014) | Extracted DNA | The analysis of DNA extracted to obtain full DNA profile from tear and tear mixture. |
| Wickenheiser RA, Jobin RM. (1999) | Contact lens | Corneal epithelial DNA can be analyzed for forensic context. |
Conclusion
The ophthalmic aids such as spectacles (colour, frame shape, dimensions, prescription etc.), contact lenses, etc. have proved to hold a good evidentiary value in the crime scene investigation as they can give the idea about the gender, age, type of refractive error in the eye. In many cases, it has been reported that the fragments of the lens give a positive match with the prescription data. The refractive error of an unknown lens can be measured by using the different type of foci meter or vertometer. So tear, spectacles, contact lenses Eyewear prescription databases act as excellent forensic evidences in crime investigation and personal identification. The ocular surface changes also help to determine the time since death.
References
- Abboud A. Daubert v. merrell dow pharmaceuticals, inc.(1993). Embryo Project Encyclopedia. 2017.
- Avisar R. Tear secretion in patients with nonspecific eye complaints. Israel J Med Sci. 1978;14:339-41.
- Baatz S. Leopold and Loeb’s Criminal Minds. Smithsonian Magazine. 2008.
- Baier G. Analysis of human tear proteins by different high-performance liquid chromatographic techniques. J Chromatogr A. 1990; 525:319-28.
- Berg GE, Collins RS. Personal Identification Based on Prescription Eyewear. J Forensic Sci. 2007; 52(2):406-11.
- Berg GE, Ta’ala SC. Predicting Biological Profiles from Prescription Eyewear: A Pilot Study. J Forensic Identif 2009;59(1):205.
- Bertolli E, Forkiotis C, Pannone D, et al. Ophthalmic appliances in identification: information retrieved from spectacles and contact lenses. J Forensic Identif. 2006;56:540-8.
- Bertolli RE, Forkiotis C, Pannone DR, et al. A Behavioral Optometry/Vision Science Perspective on the Horizontal Gaze Nystagmus Exam for DUI Enforcement. EBSCO 2007;16(1): 26-3.
- Bertolli RE, Berg GE, Pannone DR, et al. Vision Science Identification Overview. The Forensic Examiner. 2016;22(1):24-4.
- Brunish R. The protein components of human tears. Arch Ophthalmol. 1957;57:554.
[Crossref]