Case Report - Case Reports in Surgery and Invasive Procedures (2018) Case Reports in Surgery and Invasive Procedures (Special Issue 1-2018)
Laproscopic Management of Esophageal Duplication Cysts Presenting in Adults
Amarjothi JMV*, Jeyasudason J, Ramasamy V, Naganath Babu OL
Madras Medical College, EVR Salai, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Amarjothi JMV
Madras Medical College EVR Salai, 600003 Chennai, Tamil Nadu India
Tel: 9840375953
E-mail: drmosesvikramamarjothi@hotmail.com
Accepted on October 25, 2018
Citation: Amarjothi JMV, Jeyasudason J, Ramasamy V, et al. Laproscopic management of esophageal duplication cysts presenting in adults. Case Rep Surg Invasive Proced. 2018;2(3): 1-3.
Abstract
Gastrointestinal duplications are commonly seen in children involving the esophagus in about 20% of all cases. However, Esophageal duplication cysts are a rare cause of dysphagia in adults. We report a case of oesophageal duplication cysts in adult. This case report is presented mainly to describe that these predominantly congenital lesions may be symptomatic in adults and if so, must be treated expediously by surgical resection to prevent further complications.
Keywords
Cyst, Endoscopic ultrasound, Dysphagia, Computed tomography.
Introduction
Gastrointestinal duplications are commonly seen in children involving the esophagus in about 20% of all cases. Esophageal duplication cysts (EDCs) are congenital malformations of the posterior primitive foregut and often within the thoracic esophagus. Duplication cysts are congenital cystic malformation of the alimentary tract consisting of a duplication of the segment to which it is adjacent. Esophageal duplication cysts are the result of faulty intrauterine recanalization of the oesophagus and may account for 20% of all the gastrointestinal duplication cysts. Resection of oesophageal cysts is the treatment of choice, where excision of the cyst must take place with preserving the existing oesophageal mucosal and muscle integrity, and vagal nerves. In this case report, we describe the case of a 45-yearold female patient presented with progressive dysphagia, the diagnosis and its treatment.
Case Report
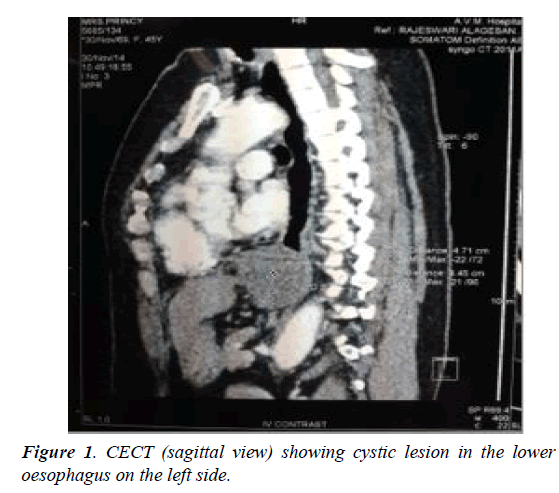
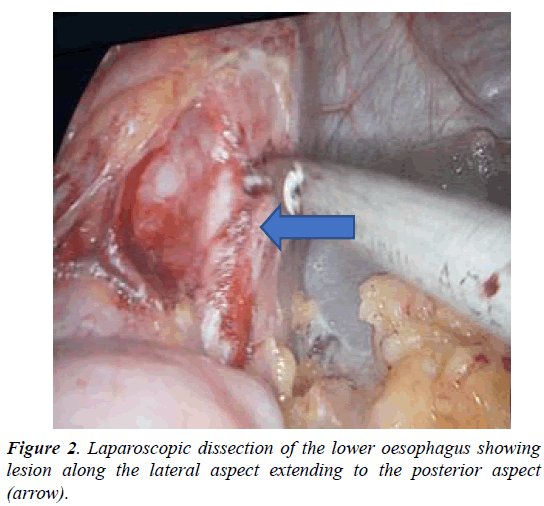
A 45-year-old female patient presented with progressive dysphagia for 1 month. And history of regurgitation for 15 days. OGD revealed an extraneous impression in the posterior aspect of the terminal oesophagus just at the GE junction. Barium swallow showed a filling defect with sharp border in distal esophagus with slight displacement of the esophagus. CT chest showed well defined enhancing mass lesion of size 4.6 × 4.3 × 4.2 cm in the lower end of the esophagus extending into gastroesophageal junction. Dilatation of proximal esophagus is seen. Multiple endoscopic biopsies were negative and inconclusive. Intraoperatively, Lesion of size 4 cm noted in the distal esophagus adherent to the lower oesophagus along the left lateral and posterior aspects. laparoscopic transhiatal extramucosal excision done by a longitudinal incision made over the distal end of the esophagus and the lesion enucleated. The mucosa of the oesophagus was found to be intact and the seromuscular defect closed with 2-0 vicryl, the lesion retrieved and sent for HPE which was suggestive of oesophageal duplication cyst where the Cyst wall was lined by pseudostratified columnar eithelium with underlying thick fibrocollagen and of circular and longitudinal smooth muscle and patient is on follow up. On 3rd POD Gastrografin study was done - No e/o leak and oral fluids was started (Figures 1 and 2).
Esophageal duplication cysts are the result of faulty intrauterine recanalization of the oesophagus and may account for 20% of all the gastrointestinal duplication cysts [1]. Based on their shape, they can be cystic (most common) or tubular and are seen most commonly involving the lower part esophagus (60%) [2]. Although most cystic duplication cysts are non-communicating, tubular duplications may occasionally communicate directly with the esophageal lumen [3].
Discussion
The esophageal duplication cysts are usually asymptomatic and are rarely symptomatic. These rare symptoms may include dysphagia, chest pain, and are seen in children [4]. Other anomalies in these patients include concurrent vertebral anomalies [5] and other duplication cysts elsewhere in the alimentary tract also [6]. The differentials for esophageal duplication cyst may include specific mediastinal cysts like bronchogenic cysts, pericardial cysts or cystic degeneration of mediastinal tumors or other cysts including hydatid cyst, muellerian cysts [7].
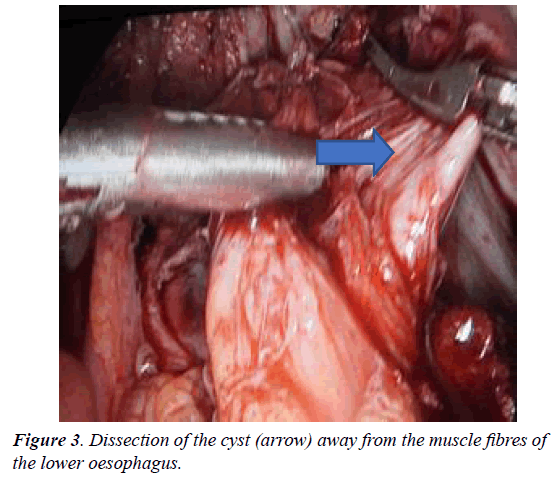
The diagnosis is usually suspected on computed tomography, which classically may present as homogenous lesion with regular margins [1]. Hypodense or heterodense lesions may occur in the presence of pus, blood or thick insipid and result in diagnostic confusion [8,9]. EUS specifically characterize these lesions and distinguishes them from bronchogenic cysts by the following specific features namely the proximity to the esophagus, double muscle layer around cyst and due to nonvisualisation of cartilage in these cysts [10] (Figure 3).
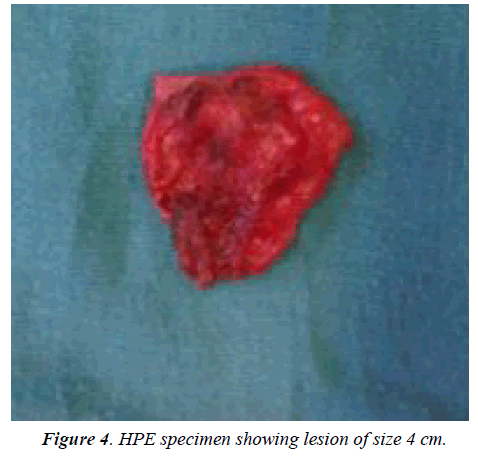
Complications in oesophageal duplication cysts are rare causing haemorrhage [11], perforation, infection, malignant transformation [12,13] and even rupture [14] (Figures 4 and 5). EUS guided FNA has been used to confirm the diagnosis but EUS FNA may lead on to infection which may be refractory to the usage of prophylactic antibiotics [15]. Therefore, caution must be borne when planning EUS FNA in patients with esophageal duplication cysts.
Conclusion
Resection of oesophageal cysts is the treatment of choice, where excision of the cyst must take place with preserving the existing oesophageal mucosal and muscle integrity, and vagal nerves [15]. Pathologically, these cysts are lined by mucous membrane with smooth muscle in their wall [6]. Ectopic gastric mucosa may be found in as many as 43% of patients [16]. Presence of other ectopic tissue like that of the pancreas is quite rare [17].
References
- Jang KM, Lee KS, Lee SJ. The spectrum of benign esophageal lesions: Imaging findings. Korean J Radiol 2002;3:199-210.
- O’Keefe JJ, Simonian S. Duplication of the esophagus. Ann Otolaryngol. 1981;90:392-95.
- Kim YS, Park CK, Choi YW, et al. Esophageal tubular duplication complicated by intraluminal hematoma: A case report, J Korean Med Sci. 2000:15:463-66.
- Wiechowska-Koz?owska A, Wunsch E, Majewski M. Esophageal duplication cysts: Endosonographic findings in asymptomatic patients. World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:1270-72.
- Estefan Ventura D, Reibscheid S, Colleoni R. Surgical images: Soft tissue. Tubular duplication of the esophagus. Can J Surg 2008;51:205-06.
- Ravitch MM, Sabiston DC. Mediastinal infections, cysts and tumours. Cysts of foregut origin, in: M. M. Ravitch, Welch KJ, Benson CD, et al. (Eds.), Pediatric Surgery, 3rd ed, Year BK Med, Chicago, 1979; pp. 500-502.
- Gümü? M, Önder A, Firat U. Hydatid cyst-like intraabdominal esophageal duplication cyst in an endemic region. Turk J Gastroenterol 2011;22:557-58.
- Diehl DL, Cheruvattath R, Facktor MA. Infection after endoscopic ultrasound-guided aspiration of mediastinal cysts. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10:338-40.
- Mansard MJ, Rao U, Rebala P. Esophageal duplication cyst masquerading as a stromal tumor in an adult. Indian J Surg. 2011;73:441-43.
- Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Wang KP. Esophageal duplication cyst: CT and transesophageal needle aspiration. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985;145:531-32.
- Peiper M, Lambrecht W, Kluth D. Bleeding esophageal duplication detected in utero. Ann Thorac Surg 1995;60:1790-91.
- Singh S, Lal P, Sikora SS. Squamous cell carcinoma arising from a congenital duplication cyst of the esophagus in a young adult. Dis Esophagus. 2001;14:258-61.
- Tapia RH, White VA. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a duplication cyst of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 1985;80:325-29.
- Neo EL, Watson DI, Bessell JR. Acute ruptured esophageal duplication cyst. Dis Esophagus 2004;17:109-11.
- Cioffi U, Bonavina L, De Simone M, et al. Presentation and surgical management of bronchogenic and esophageal duplication cysts in adults. Chest. 1998;113:1492-96.
- Macpherson RI. Gastrointestinal tract duplications: clinical, pathologic, etiologic, and radiologic considerations. Radiographics. 1993;13:1063-80.
- Qazi FM, Geisinger KR, Nelson JB, et al. Symptomatic congenital gastroenteric duplication cyst of the esophagus containing exocrine and endocrine pancreatic tissues. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990;85:65-67.