Clinical Image - Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine and Therapeutics (2018) Volume 2, Issue 3
Intramural aortic hematoma as a cause of chest pain.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Azahara Fernández Carbonell
Cardiovascular Surgery Service, Reina Sofía University Hospital Córdoba, Spain
Tel: +34 662194496
E-mail: azasa89@hotmail.com
Accepted date: Sept 28, 2018
Citation: Azahara Fernández Carbonell, Alados Arboledas Pedro, Rodríguez Guerrero Enrique, et al. Intramural aortic hematoma as a cause of chest pain. J Cardiovasc Med Ther 2018;2(2):9
Abstract
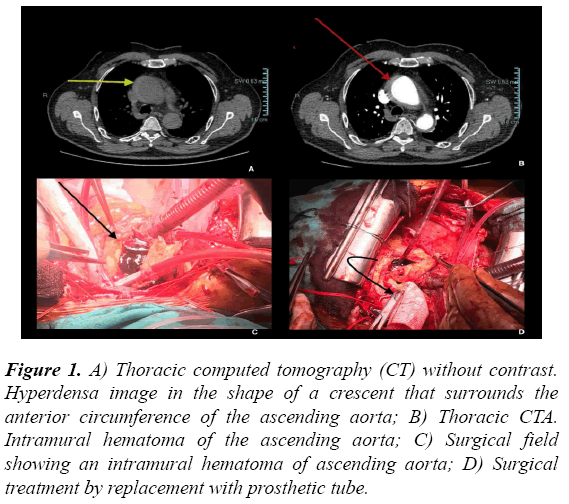
Intramural aortic hematoma is included within the acute aortic syndrome, along with aortic dissection and arteriosclerotic penetrating ulcer. We present the case of a 62-year-old patient who began with a chest pain clinic that did not respond to the usual analgesia, and who was subsequently operated on by an intramural aortic hematoma, after the diagnosis by CT and echocardiography (Figure 1).
Clinical Image
Intramural aortic hematoma is included within the acute aortic syndrome, along with aortic dissection and arteriosclerotic penetrating ulcer. We present the case of a 62-year-old patient who began with a chest pain clinic that did not respond to the usual analgesia, and who was subsequently operated on by an intramural aortic hematoma, after the diagnosis by CT and echocardiography (Figure 1).
Figure 1: A) Thoracic computed tomography (CT) without contrast. Hyperdensa image in the shape of a crescent that surrounds the anterior circumference of the ascending aorta; B) Thoracic CTA. Intramural hematoma of the ascending aorta; C) Surgical field showing an intramural hematoma of ascending aorta; D) Surgical treatment by replacement with prosthetic tube.